Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка
Title: Enhancing Precision and Control with Wheel Encoder Sensors In the realm of industrial automation and robotics, precision and accuracy are paramount. One of the key components that ensure these qualities in motion control systems is the wheel encoder sensor. This article delves into the significance of wheel encoder sensors, their functioning, and their critical role in enhancing precision and control across various applications.
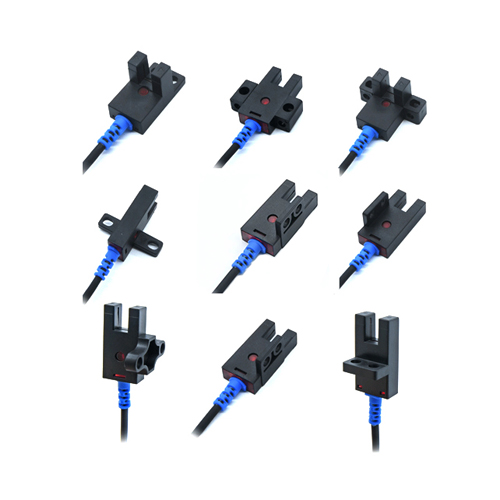
Wheel encoder sensors, often referred to as wheel encoders, are devices used to monitor the position and speed of a rotating wheel or shaft. They are integral parts of many motion control systems, including those found in robotics, CNC machines, conveyor belts, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs). These sensors work on the principle of converting mechanical movement into electrical signals that can be interpreted by a control system for feedback purposes.

There are primarily two types of wheel encoder sensors: incremental and absolute. Incremental encoders provide information about the direction and relative position change of the wheel by generating a series of pulses corresponding to each unit of rotation. Absolute encoders, on the other hand, determine the exact position of the wheel at any given time, regardless of previous movements. This data is crucial for systems requiring high precision and reliability. Incremental encoders typically employ a disc with alternating light and dark segments (a code disk) and LED/photodiode pairs to detect changes in light as the disc rotates. Each revolution results in a specific number of pulses, allowing the system to track speed and distance traveled. Absolute encoders use a more complex encoding method, often involving a circular grid of conductive and non-conductive areas, to establish a unique binary code for every possible position of the wheel.
The accuracy of wheel encoder sensors directly impacts the performance of motion control systems. Even minor deviations can lead to significant errors in positioning and timing, which can be detrimental in applications such as manufacturing, where precision is vital. High-quality wheel encoders minimize these discrepancies by using advanced technology to enhance resolution and reduce latency. Furthermore, the durability and reliability of wheel encoder sensors are essential for maintaining consistent performance over time. They must withstand harsh environmental conditions, including temperature fluctuations, vibrations, and exposure to dust and moisture. Robust construction and protective features like IP ratings ensure longevity and dependable operation in challenging settings.
Wheel encoder sensors have widespread applications across numerous industries due to their ability to provide precise motion control. In the automotive industry, they are used in electric power steering systems and anti-lock braking systems (ABS) to enhance vehicle safety and handling. In robotics, they enable smoother and more accurate movement of robotic arms and autonomous mobile robots. In manufacturing, wheel encoders play a critical role in conveyor systems and CNC machinery, ensuring products are moved and machined with the highest level of precision. They are also indispensable in the operation of elevators and escalators, where accurate speed and position control are crucial for passenger safety and comfort.
Wheel encoder sensors are fundamental components in the pursuit of precision and control within motion systems. Their ability to accurately measure and feedback position and speed information allows for enhanced performance and reliability across various applications. As technology continues to advance, the development of even more sophisticated wheel encoders will undoubtedly contribute to further advancements in automation, robotics, and beyond. With their critical role in ensuring precise motion control, wheel encoder sensors remain an indispensable asset in modern industry.