Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка
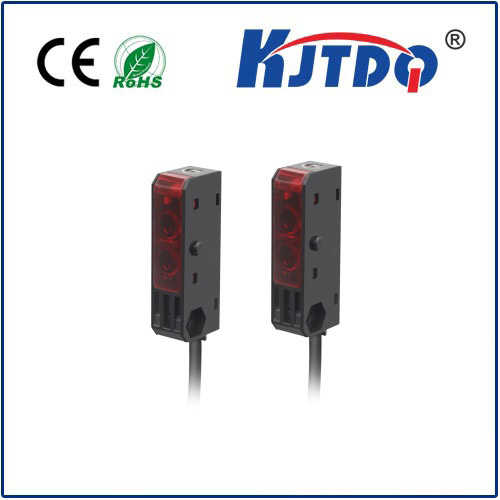
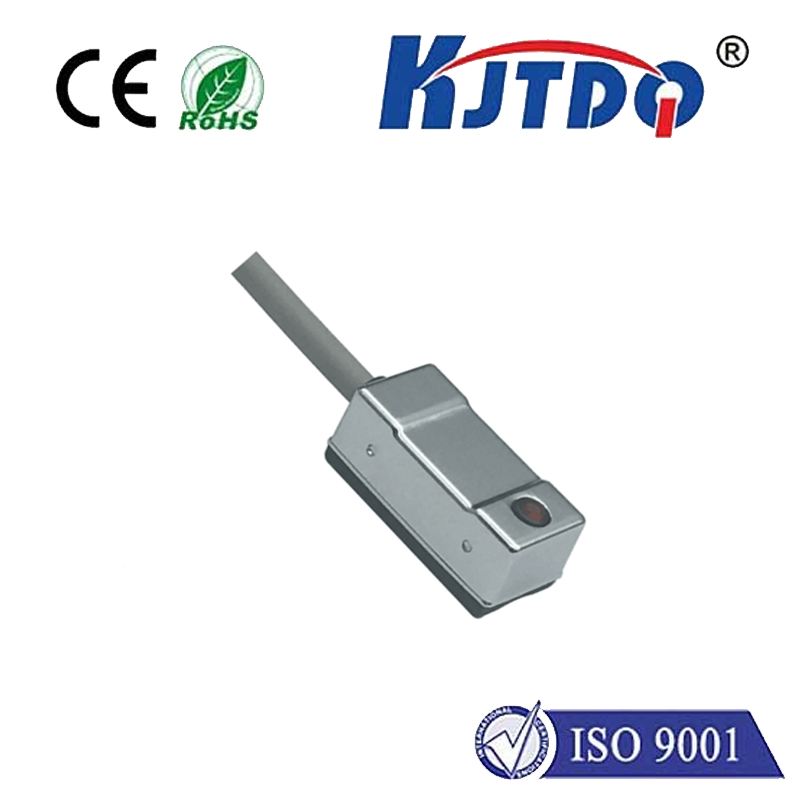
Understanding the Photoelectric Proximity Switch: A Key Component in Modern Automation In the ever-evolving world of industrial automation, precision and reliability are paramount. Among the myriad of components that ensure seamless operations, the Фотоэлектрический переключатель приближения stands out as a critical device. This sophisticated sensor, which detects the presence or absence of objects without physical contact, has become indispensable in various industries. But what exactly is a photoelectric proximity switch, and why is it so vital in today’s automated systems? Let’s delve into its workings, applications, and benefits.
А.Фотоэлектрический переключатель приближения is a non-contact sensor that uses light to detect objects within its sensing range. Unlike mechanical switches that require physical interaction, this device operates by emitting a beam of light—usually infrared or visible—and measuring the reflection or interruption of that beam. When an object enters the sensor’s field, it disrupts the light beam, triggering the switch to send a signal to the control system. There are three primary types of photoelectric proximity switches:
Through-Beam Sensors: These consist of a separate emitter and receiver. The emitter sends a light beam to the receiver, and when an object blocks the beam, the sensor detects its presence.
Retro-Reflective Sensors: These use a reflector to bounce the light beam back to the sensor. The presence of an object interrupts this reflection, signaling detection.
Diffuse Reflective Sensors: In this type, the emitter and receiver are housed together. The sensor detects the object by measuring the light reflected directly off it.
The operation of a Фотоэлектрический переключатель приближения is based on the principle of light modulation. The emitter generates a beam of light, which travels to the receiver or reflects off an object. The receiver then analyzes the light’s intensity or time of flight to determine the object’s presence or distance. For instance, in a through-beam sensor, the emitter continuously sends a light beam to the receiver. When an object obstructs the beam, the receiver detects a drop in light intensity, triggering the switch. Similarly, in a diffuse reflective sensor, the receiver measures the light reflected off the object. The sensor is calibrated to recognize specific light patterns, ensuring accurate detection.
The versatility of photoelectric proximity switches makes them suitable for a wide range of applications across various industries. Here are some of the most common uses:
Manufacturing and Assembly Lines: These sensors are integral in detecting the presence, position, or movement of components on conveyor belts. They ensure precise alignment and prevent jams or misplacements.
Packaging Industry: Photoelectric switches are used to count products, verify packaging integrity, and control the placement of labels.
Автомобильная промышленность: In vehicle assembly, these sensors monitor the position of parts, ensuring accurate installation and reducing errors.

Food and Beverage Industry: They detect the presence of containers, monitor fill levels, and ensure proper sealing of packages.
Pharmaceuticals: In this highly regulated industry, photoelectric switches play a crucial role in verifying the presence of pills, vials, or packaging materials.
The Фотоэлектрический переключатель приближения offers several advantages over traditional mechanical switches:
Non-Contact Operation: Since these sensors do not require physical contact, they eliminate wear and tear, resulting in longer lifespans.
Высокая точность: They can detect objects with millimeter accuracy, making them ideal for applications requiring fine-tuned control.
Многогранный.: These switches can detect a wide range of materials, including glass, plastic, metal, and liquids.
Fast Response Times: Photoelectric sensors operate at high speeds, making them suitable for fast-paced production lines.
Долговечность: Designed to withstand harsh industrial environments, they are resistant to dust, moisture, and temperature fluctuations.
Selecting the appropriate Фотоэлектрический переключатель приближения for your application requires careful consideration of several factors:
Sensing Range: Determine the distance over which the sensor needs to detect objects. Through-beam sensors typically offer longer ranges than diffuse reflective ones.
Object Characteristics: Consider the size, shape, and material of the objects to be detected. Some sensors are better suited for transparent or highly reflective materials.
Environmental Conditions: Evaluate the operating environment, including temperature, humidity, and exposure to contaminants.
Тип экспорта: Choose between digital or analog outputs based on your system’s requirements.
Mounting Options: Ensure the sensor can be easily integrated into your existing setup.
As technology continues to advance, photoelectric proximity switches are evolving to meet the demands of modern automation. Emerging trends include:
Miniaturization: Smaller sensors are being developed to fit into compact spaces without compromising performance.
Enhanced Connectivity: Integration with IoT (Internet of Things) platforms allows for real-time monitoring and data analysis.
Improved Durability: New materials and coatings are being used to enhance resistance to extreme conditions.
Smart Sensors: These advanced devices can self-calibrate, diagnose issues, and adapt to changing environments. In conclusion, the Фотоэлектрический переключатель приближения is a cornerstone of industrial automation, offering unparalleled precision, reliability, and versatility. Its ability to detect objects without physical contact has revolutionized countless processes, making it an essential component in modern manufacturing and beyond. As technology progresses, these sensors will continue to play a pivotal role in driving efficiency and innovation across industries.









