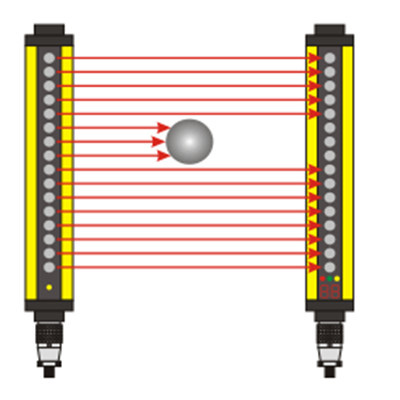
Title: Unveiling the Versatility of Low Voltage Proximity Sensors In the ever-evolving landscape of automation and control systems, the role of sensors cannot be overstated. Among the myriad options available, low voltage proximity sensors stand out for their unique capabilities and applications. These devices are designed to detect objects or surfaces without any physical contact, making them ideal for a range of industrial and commercial settings where precision and longevity are crucial. Low voltage proximity sensors operate at relatively low power levels, which makes them energy efficient and suitable for applications that require prolonged battery life or operation in environments with limited power supply. Despite their lower power consumption, these sensors do not compromise on performance, offering reliable detection across varying distances and conditions. One key advantage of low voltage proximity sensors is their ability to function in harsh environments. Whether exposed to moisture, dust, or extreme temperatures, these sensors maintain consistent operation. This resilience is particularly valuable in industries such as manufacturing, logistics, and automotive, where environmental conditions can be challenging and unpredictable. Another significant benefit is their compact size, allowing for integration into tight spaces without sacrificing functionality. This characteristic enables engineers and designers to implement sophisticated control systems within confined areas, such as within machinery or alongside other sensitive components. Furthermore, low voltage proximity sensors support a variety of sensing technologies including capacitive, inductive, and photoelectric. Each type has its own set of advantages depending on the application requirements. For instance, inductive sensors are well-suited for metal detection, while capacitive sensors excel at identifying non-metallic materials and liquids. Photoelectric sensors, on the other hand, are often used in applications requiring high precision and speed. The versatility of low voltage proximity sensors extends to their output options. They can provide either digital or analog signals based on the needs of the system they are part of. Digital outputs are typically binary, offering a simple on/off signal that is easy to interface with most control systems. Analog outputs, on the other hand, provide variable signals that can offer more detailed information about the detected object’s properties, such as distance or size. Installation and maintenance of low voltage proximity sensors are generally straightforward, further adding to their appeal. Many models come with user-friendly features such as adjustable sensing distances and built-in indicators for status monitoring. Some even include diagnostic tools that facilitate troubleshooting and ensure optimal performance over time. In conclusion, low voltage proximity sensors represent a significant advancement in sensing technology, providing a reliable, versatile, and cost-effective solution for various detection needs. Their efficiency, durability, and adaptability make them an invaluable asset in today’s automated environments. As industries continue to innovate and demand higher levels of performance from their equipment, the role of these sensors is likely to expand even further, driving progress and enhancing operational capabilities across diverse sectors.