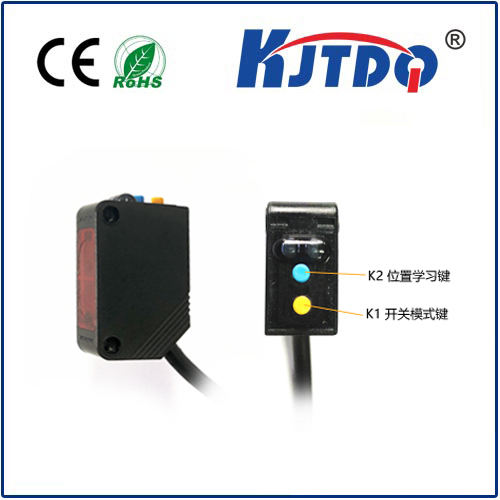
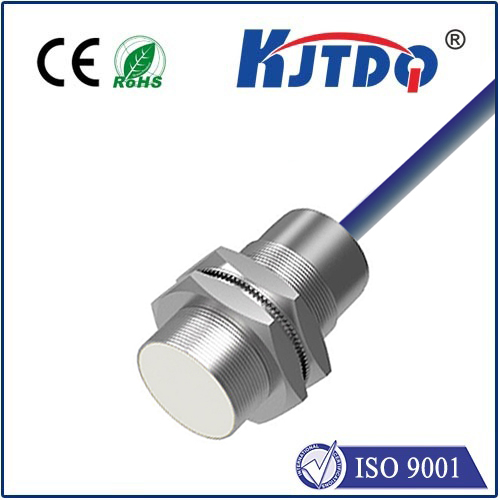
электронный датчик приближения
- time:2025-01-23 01:06:40
- Нажмите:0

Understanding the Electronic Proximity Sensor: A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s technologically driven world, electronic proximity sensors play an essential role in various applications spanning from industrial automation to consumer electronics. As a versatile and precise tool for detecting the presence or absence of objects without physical contact, these sensors have revolutionized how we interact with machines and devices. In this article, we will delve into what electronic proximity sensors are, how they work, their types, and their diverse applications.
What is an Electronic Proximity Sensor?
An electronic proximity sensor is a device designed to detect the proximity or presence of an object within a certain range without any physical touch. It utilizes principles such as electromagnetic fields, capacitive coupling, or optical technology to sense changes in the surrounding environment. When an object comes within its sensing range, the sensor generates an electrical signal that can be further processed or used to trigger specific actions. These sensors are highly effective in environments where mechanical contact may be impractical, damaging, or unsafe.
How Do Electronic Proximity Sensors Work?
The functioning of electronic proximity sensors depends on the type of technology employed. Here are the most common types along with brief explanations of their working principles:
- Inductive Proximity Sensors: These sensors operate based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. An oscillator circuit generates a high-frequency electromagnetic field which, when interrupted by a conductive object, causes a change in the oscillation amplitude. This change is detected and converted into an electrical output signal.
- Capacitive Proximity Sensors: These sensors use changes in capacitance to detect objects. They consist of a conductive plate (sensor electrode) and an insulating housing. The presence of an object alters the dielectric constant between the electrode and the object, leading to a change in capacitance. This variation is measured and converted into an output signal.
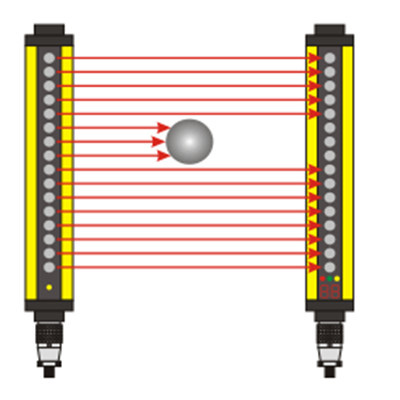
- Photoelectric Proximity Sensors: These sensors rely on light to detect objects. They consist of an emitter that projects light (usually infrared) and a receiver that detects the reflected light from the target object. If an object interrupts the light path or reflects it differently, a signal is generated.
Applications of Electronic Proximity Sensors
The versatility of electronic proximity sensors makes them indispensable in numerous industries and applications:
- Промышленная автоматизация: Proximity sensors ensure accurate positioning, counting, and monitoring of products in manufacturing processes, thereby enhancing efficiency and safety.
- Consumer Electronics: From smartphones to home appliances, proximity sensors enable features like auto screen shutdown, touchless control, and enhanced user interface experiences.
- Security Systems: These sensors are crucial in alarm systems and motion detectors, providing reliable security solutions by detecting unauthorized entries or movements.
- Transportation: In vehicles, proximity sensors facilitate functionalities such as parking assistance, collision avoidance systems, and automatic door mechanisms.
- Medical Field: They are used in medical equipment for patient monitoring and ensuring precision in diagnostic and surgical instruments.
Выводы
Electronic proximity sensors represent a remarkable advancement in sensing technology, offering non-contact detection that enhances safety, reliability, and efficiency across a broad spectrum of applications. Understanding their types and working principles allows us to harness their potential effectively, driving innovation and improvement in both everyday devices and complex industrial systems. As technology continues to evolve, the role of electronic proximity sensors is set to expand even further, paving the way for smarter, more responsive environments.