криогенный ограничитель
- time:2025-08-01 12:35:43
- Нажмите:0
The Essential Guardian Against Freeze Damage: Understanding Low Temperature Limit Switches
Imagine the heart of a commercial refrigeration system failing on the coldest night of the year. Icy water floods a critical manufacturing process because a pipe burst. Or worse, a building’s automatic fire sprinkler system freezes solid, rendering it useless in an emergency. These catastrophic scenarios often have a common, preventable root cause: uncontrolled low temperatures. Enter the unsung hero – the криогенный ограничитель. This small, robust device stands as a critical sentinel, constantly monitoring ambient or surface temperatures and acting decisively to prevent potentially devastating freeze damage.
What Exactly is a Low Temperature Limit Switch?
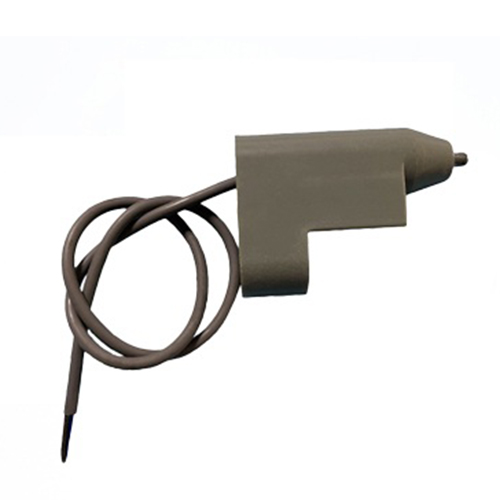
At its core, a криогенный ограничитель is a specialized temperature-activated safety control. It functions as a vigilant guard, specifically tasked with detecting when temperatures drop below a predetermined, safe threshold—known as the fixed setpoint. Unlike programmable thermostats that manage heating or cooling cycles, this switch has a singular, vital mission: freeze protection.

Its operation follows a crucial sequence:
- Sensing: An internal temperature-sensitive element (commonly a snap-action bimetallic disc or a bulb-and-capillary system filled with a gas or fluid) continuously monitors the target environment or surface.
- Threshold Detection: When the sensed temperature plunges below the factory-calibrated (or sometimes field-adjustable) low-limit setpoint, the internal mechanism reacts.
- Action: The reaction triggers a change in the state of its electrical contacts (typically Normally Closed - NC - or Normally Open - NO). This switch is most commonly configured to open a circuit when the low-limit temperature is breached.
- System Response: This break in the electrical circuit sends a signal to the system’s control logic or directly interrupts power to critical components (like fans or compressors in HVAC systems), forcing a shutdown or initiating corrective measures (like enabling heaters).
Where Does This Frozen Shield Prove Essential?
The криогенный ограничитель is indispensable across numerous industries where uncontrolled chilling spells disaster:
- HVAC/R Systems: This is arguably its most common battleground.
- Air Handling Units (AHUs) & Ductwork: Preventing the freezing of cooling coils during off-seasons or economizer operation in cold weather. A frozen coil can rupture, leading to costly water damage and system downtime.
- Heat Pumps: Protecting outdoor coils from freezing up during the defrost cycle or unusually cold operation.
- Commercial Refrigeration: Safeguarding components like condensate pans from freezing and overflowing, potentially causing slip hazards or water damage.
- Chilled Water Systems: Preventing ice formation in pipes or critical components if water flow stops unexpectedly in low ambient conditions.
- Industrial Processes:
- Process Cooling: Ensuring cooling fluids or process lines don’t fall below a critical temperature, which could alter product viscosity, cause crystallization, or damage sensitive equipment. Maintaining thermal stability is often paramount.
- Fluid Storage Tanks: Preventing water-based solutions, chemicals, or fuels from freezing inside storage vessels, which can cause expansion damage or alter chemical properties.
- Instrumentation Air: Shutting down systems if compressed air lines risk freezing due to moisture and low temperatures, preventing blockages and equipment failure.
- Building & Life Safety:
- Fire Sprinkler Systems: Arguably one of its most critical roles. Installed in valve rooms or areas prone to freezing, it triggers alarms or activates backup heating if temperatures threaten to freeze pipes. A frozen sprinkler system is catastrophic in a fire event.
- Water Pipes: Protecting vulnerable water lines in unheated spaces like attics, crawl spaces, or garages.
- Transportation:
- Protecting onboard systems in vehicles (e.g., buses, specialized equipment) from low-temperature damage during operation or storage.
Core Functions: More Than Just an “Off” Switch
While interrupting system operation is its primary safety function, a криогенный ограничитель often delivers additional critical benefits:
- Safeguarding Equipment: The foremost role is preventing physical damage. Freezing water expands by roughly 9%, easily capable of splitting pipes, cracking coils, rupturing tanks, or damaging sensitive components like compressor valves. The switch acts before this destructive expansion can occur.
- System Protection: Beyond physical damage, freezing can severely disrupt system hydraulics (blocked pipes), reduce efficiency (iced-over coils), and lead to compressor slugging or burnout in refrigeration systems. The switch preempts these cascade failures.
- Triggering Alarms & Secondary Actions: Many switches incorporate alarm contacts or signal outputs. When the low limit is breached, they can activate warning lights, audible alarms, or building management system (BMS) alerts, prompting immediate human intervention. They may also directly activate auxiliary freeze protection heaters.
- Automatic Reset (& Manual Override): Most standard low temperature limit switches feature automatic reset. Once the temperature climbs safely above the setpoint (often by a few degrees to prevent rapid cycling), the contacts return to their normal state, allowing the system to restart automatically. Some critical applications might utilize a manual reset version, requiring a physical button press after an alarm condition, ensuring the cause is investigated before restarting.
Choosing Your Frozen Frontier Defender: Key Considerations
Selecting the right криогенный ограничитель involves more than just picking a number:
- Temperature Setpoint: Crucial! What is the absolute minimum safe temperature before damage occurs? Consider the fluid’s freezing point and add a safety margin. Typical setpoints range from +5°C down to -40°C or lower. Choosing too close to the actual freezing point is risky.
- Differential: Often fixed, but adjustable on some models. This is the temperature rise required above the setpoint for the switch to reset after tripping. A wider differential prevents rapid, damaging cycling.
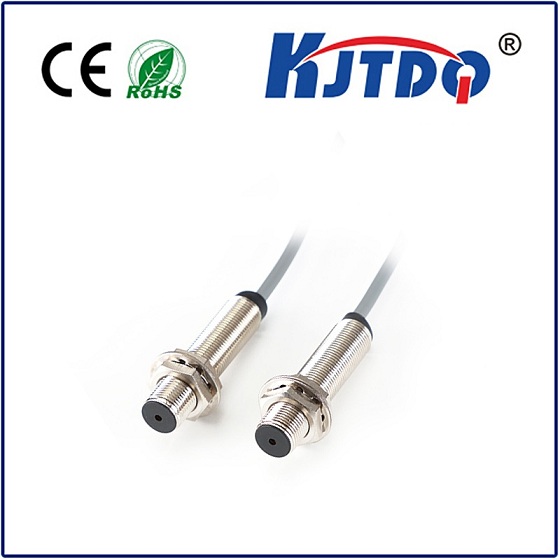
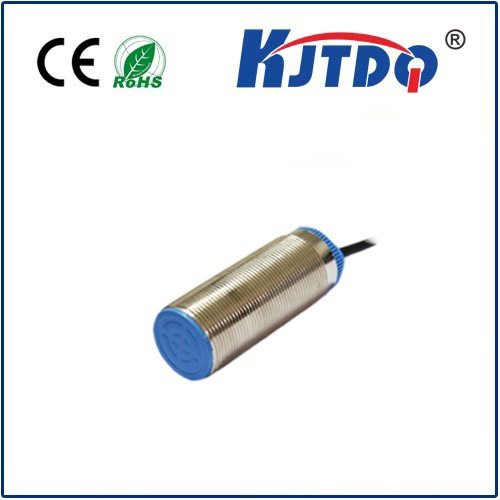
- Application Environment: Will it measure ambient air? Surface temperature? Immersed in liquid? Choose the correct sensing element type (bulb, capillary, direct immersion probe) and probe length/material (e.g., brass, stainless steel). Consider corrosive atmospheres or washdown needs.
- Electrical Rating: Ensure the switch contacts (voltage and current rating - AC or DC) can handle the load they are controlling (relay coil, starter coil, alarm circuit, heater).
- Enclosure & Ratings: Protection against environmental factors (NEMA rating for dust/water, IP rating) is vital, especially in harsh or outdoor locations. Consider explosion-proof requirements if necessary.
- Contact Configuration: Normally Closed (NC - opens on alarm) is standard for safety shutdown circuits. Normally Open (NO - closes on alarm) is less common but used for specific alarm triggering functions. SPDT offers