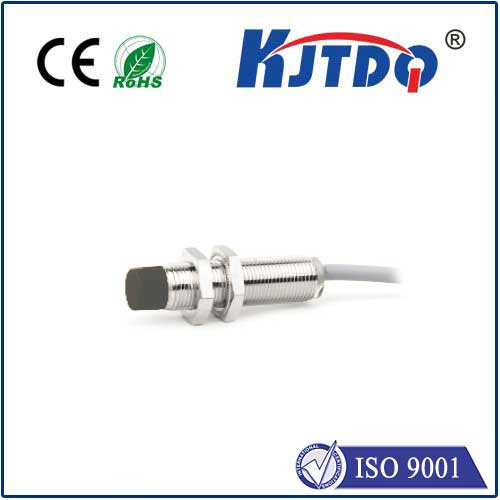
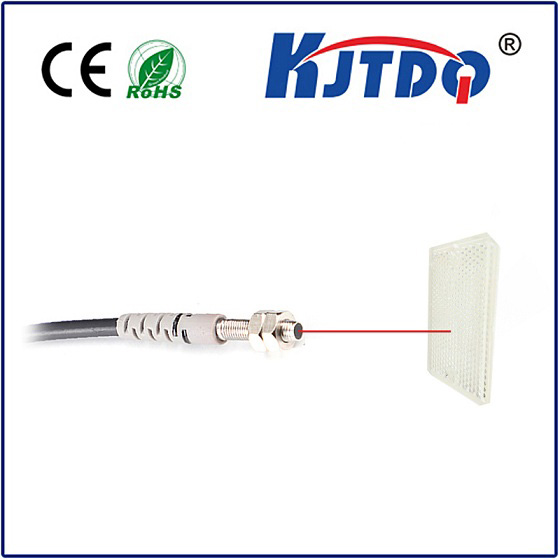
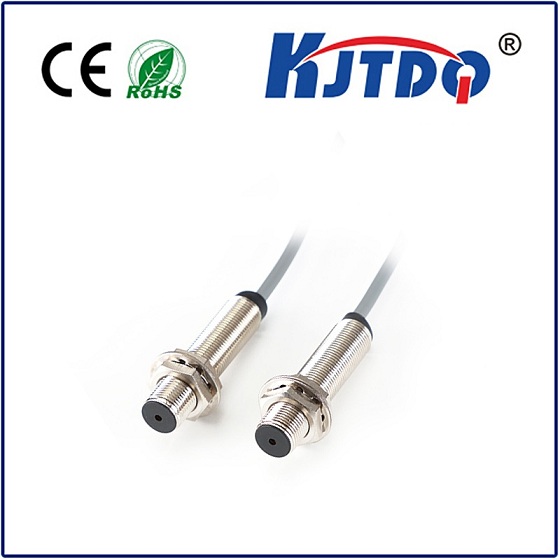
Proximity switches are very useful devices in industrial environments that detect the presence of certain objects and help control and monitor processes, helping to increase productivity and efficiency.

Let's take a closer look at the proximity switch model, which consists of the following parts:
Part 1 is the code name of the proximity switch. This code represents the type of proximity switch. For example, LJ stands for sensitive proximity switch, CJ stands for capacitive proximity switch, and SJ stands for Hall effect proximity switch.
Part 2 introduces the structural form of the proximity switch. For example, M stands for cylinder, B stands for small square, and D stands for regular.
Part 3 deals with sensitive forms of proximity switches. These models also have parameters describing sensing distance and power source type. Users should pay special attention to the meaning of the last parameter. This parameter represents the output format.
Proximity switches generally have two output forms. One is NPN output and the other is PNP output.
For example, proximity switch KJTLJM18T-5Z/N: KJT represents the sensor brand KJT, and LI represents the sensitive proximity switch. Its shape is M18, which means cylindrical. T stands for embedded sensitive form. The 5Z at the back indicates that the detectable distance is 5 mm, and the last item NK indicates that the proximity sensor is an NPN normally open proximity switch.
Proximity switches are used in various industrial fields. They play an important role in various applications including the automotive and electronics industries. Proximity switches have become an integral part of plant and machine automation.
Information about proximity switch models will help you make the right product choice. By understanding the characteristics and functions of proximity switches, you can choose the appropriate proximity switch. Thereby improving work efficiency and making the production process proceed smoothly.