Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

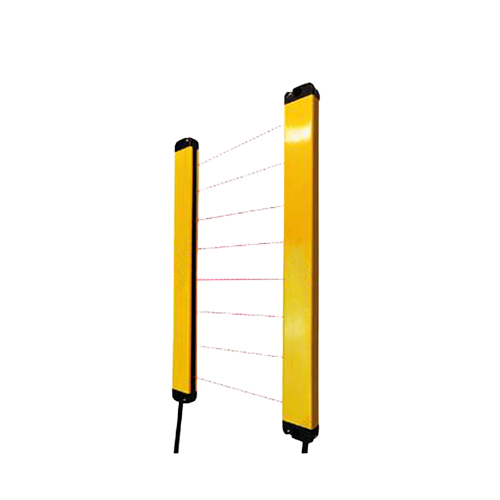
Title: An In-Depth Look at Types of Non-Contact Proximity Switches In the realm of automation and industrial sensing, non-contact proximity switches play a pivotal role. These devices are essential for detecting the presence or absence of objects without making physical contact, thus ensuring longevity and precision. Let’s delve into the various types of non-contact proximity switches and their unique characteristics. Capacitive Proximity Switches Capacitive proximity switches operate based on the principle of capacitance. They consist of a conductive plate and an insulator, which create an electric field. When an object with a different dielectric constant (such as metal or plastic) enters this field, it alters the capacitance, triggering the switch. These switches are highly versatile, capable of detecting various materials including liquids, powders, and granular substances. They are ideal for applications requiring high sensitivity and accuracy, such as level monitoring in liquid containers or detecting the presence of small components in manufacturing processes. Inductive Proximity Switches Inductive proximity switches work based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. They consist of an oscillator that generates an electromagnetic field and a sensor coil. When a metallic object comes within range of this field, it induces eddy currents within the object, causing a change in the oscillation frequency of the coil and activating the switch. These switches are widely used in environments where reliability and durability are paramount. They are resistant to dust, dirt, and oil, making them suitable for harsh industrial settings such as automotive manufacturing, packaging machinery, and conveyor systems. Magnetic Proximity Switches Magnetic proximity switches utilize magnetism to detect ferrous (iron-based) materials. A magnetic field is created by a permanent magnet or an electromagnet within the switch. When a ferrous object approaches, it disrupts the magnetic field, causing the internal reed switch to activate. These switches are particularly useful in applications where detecting only ferrous materials is necessary, such as sorting metal from non-metal items or monitoring the position of iron gates or doors. Photoelectric Proximity Switches Photoelectric proximity switches function using light beams. They come in two main types: through-beam and retroreflective. In through-beam configurations, a transmitter emits a light beam towards a receiver, and when an object interrupts this beam, the receiver signals the switch. Retroreflective switches, on the other, have both the emitter and receiver in the same unit; the light beam reflects off a mirror back to the receiver. Photoelectric switches are excellent for detecting transparent or reflective objects, and they are commonly employed in applications requiring precise positioning and alignment, such as web tension control or label inspection systems. Выводы Non-contact proximity switches offer a diverse range of solutions for various industrial needs, from capacitive and inductive sensors to magnetic and photoelectric varieties. Each type has its own set of advantages and is best suited for specific applications. By understanding these differences, manufacturers can select the most appropriate switch for their particular requirements, enhancing efficiency and productivity in their operations