Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка
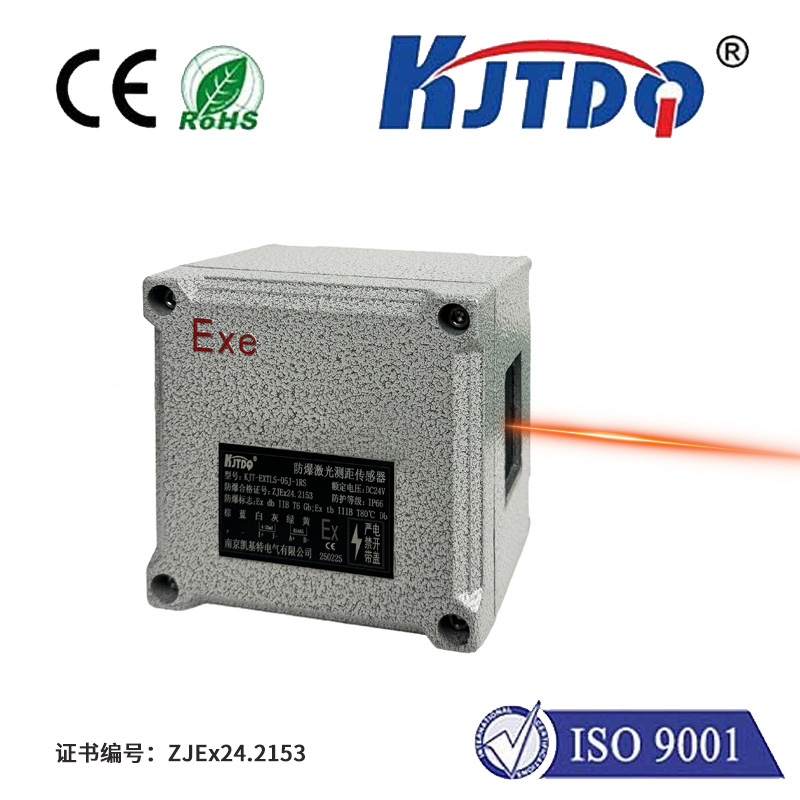
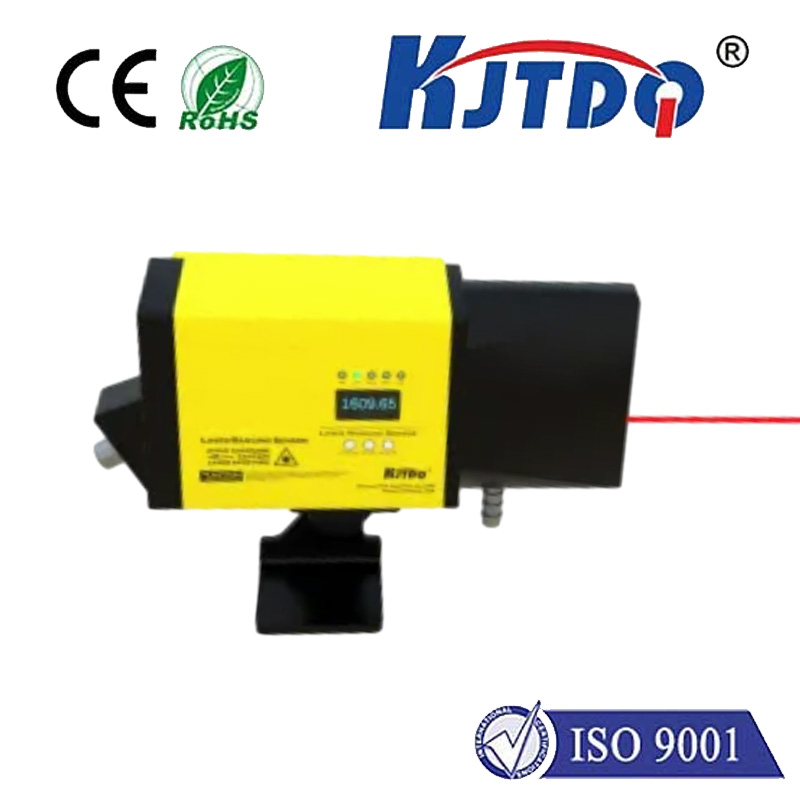
In the world of modern engineering, construction, and automation, the ability to measure distance with pinpoint accuracy is not just a convenience—it's a fundamental requirement. This is where the Distance Measurement Laser Rangefinder Sensor steps into the spotlight. Far more than a simple measuring tape for the digital age, this sophisticated device harnesses the power of laser technology to deliver non-contact, high-speed, and exceptionally precise measurements across a vast array of applications.
At its core, a laser rangefinder sensor operates on a straightforward yet brilliant principle: time-of-flight. The sensor emits a focused pulse of laser light towards a target. This light reflects off the surface and returns to a receiver within the sensor. By calculating the incredibly short time interval between the emission and the reception of the laser pulse, and knowing the constant speed of light, the sensor's internal processor can determine the exact distance to the target with remarkable accuracy. This process happens in milliseconds, enabling real-time data acquisition that is critical for dynamic systems.
The advantages of using a laser rangefinder sensor are transformative. First and foremost is its unparalleled precision. Capable of achieving accuracies within millimeters or even sub-millimeter ranges, it eliminates the human error inherent in manual measurement tools. Its non-contact nature is another significant benefit. It can safely measure distances to hazardous, fragile, or inaccessible objects without any risk of damage or contamination. This makes it indispensable in environments like high-voltage areas, clean rooms, or when measuring hot surfaces in industrial settings.
Furthermore, these sensors offer exceptional speed and range. Measurements are taken almost instantaneously, which is vital for applications involving moving objects or automated processes. Modern sensors can measure distances from a few centimeters up to several hundred meters, catering to both intimate precision tasks and large-scale surveying needs. Their robustness is also notable; many models are designed to withstand harsh industrial environments, resisting dust, moisture, and vibration.
The practical applications of Distance Measurement Laser Rangefinder Sensors are vast and growing. In industrial automation, they are crucial for robotics, providing real-time positioning data for robotic arms in assembly lines, ensuring precise part placement and collision avoidance. In logistics and warehousing, they automate inventory management by measuring stock levels and guiding automated guided vehicles (AGVs) through storage facilities. The construction and surveying industries rely on them for land surveying, building layout, and monitoring structural deformations with high accuracy.
Emerging fields are also leveraging this technology. In autonomous vehicles, laser rangefinders, often as part of LiDAR systems, create detailed 3D maps of the surroundings to navigate safely. In agriculture, they assist in monitoring crop growth and guiding automated machinery. Even in consumer electronics, they enable features like camera autofocus and augmented reality applications.
When selecting a laser rangefinder sensor, several key specifications demand attention. The measuring range and accuracy are paramount and must align with the specific task. The response time determines how quickly the sensor can update its readings, which is critical for high-speed automation. Environmental ratings, such as IP protection for dust and water resistance, ensure reliability in challenging conditions. Output interfaces, like analog voltage, current loops, or digital protocols (RS232, USB, Ethernet), define how the sensor integrates with existing control systems and data loggers.
Looking ahead, the evolution of laser rangefinder sensor technology points towards even greater miniaturization, enhanced accuracy over longer distances, and reduced power consumption. Integration with artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things (IoT) is set to unlock smarter, more autonomous systems that can interpret distance data in context and make independent decisions.
In conclusion, the Distance Measurement Laser Rangefinder Sensor is a cornerstone technology of precision measurement. By offering a blend of speed, accuracy, and versatility that traditional tools cannot match, it empowers industries to operate with greater efficiency, safety, and intelligence. From the factory floor to the open road, it is the unseen eye that measures our world with the unwavering consistency of light itself.