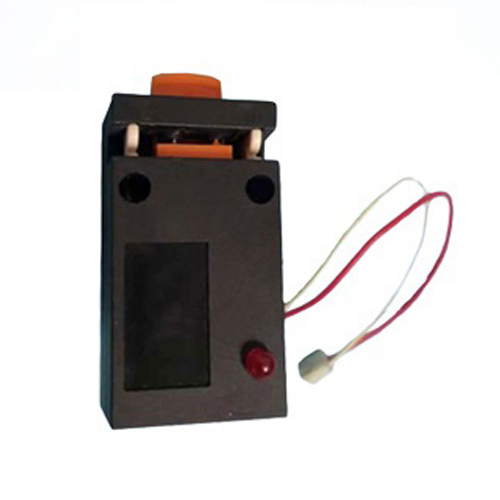
Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка
In the rapidly evolving landscape of industrial automation and smart device integration, the demand for accurate, reliable, and cost-effective distance measurement solutions has never been higher. Among the various technologies vying for dominance, CMOS laser sensor distance measurement stands out as a pivotal innovation, particularly when enhanced by advanced platforms like KJTDQ. This technology is fundamentally reshaping how machines perceive and interact with their environment, enabling new levels of operational efficiency and product intelligence.
At its core, a CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) laser sensor operates by emitting a laser beam towards a target. The sensor then captures the reflected light using a CMOS image sensor. By precisely calculating the time it takes for the light to return or by analyzing the phase shift of the modulated laser beam, the sensor can determine the distance to the object with remarkable accuracy. This method, known as time-of-flight (ToF) or phase-shift measurement, provides a non-contact, high-speed alternative to traditional mechanical or ultrasonic sensors.
The integration of this technology with the KJTDQ platform elevates its capabilities significantly. KJTDQ systems are engineered to optimize the signal processing, noise reduction, and data interpretation from the CMOS sensor. This results in enhanced performance in challenging conditions, such as low ambient light, high background noise, or with poorly reflective surfaces. For instance, in a logistics warehouse, KJTDQ-powered CMOS laser sensors can accurately measure the dimensions of packages on a fast-moving conveyor belt, ensuring correct sorting and storage without physical contact, thereby reducing wear and tear and maintenance costs.
One of the most compelling applications is in the realm of robotics and autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs). These machines rely on precise environmental mapping and obstacle detection to navigate safely. A CMOS laser sensor, processed through a KJTDQ system, can provide real-time, high-resolution distance data across a wide field of view. This allows a robot to not only avoid collisions but also to perform complex tasks like precise bin picking or assembly line assistance. The low power consumption inherent to CMOS technology, combined with KJTDQ's efficient algorithms, makes it ideal for battery-operated mobile robots.
Furthermore, the consumer electronics sector is leveraging this synergy for features like facial recognition for smartphone security and autofocus in cameras. The miniaturization potential of CMOS sensors, amplified by KJTDQ's compact processing solutions, allows for their integration into slim devices without sacrificing accuracy. In automotive applications, it forms the backbone of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), enabling functions like adaptive cruise control and pedestrian detection by creating detailed 3D maps of the vehicle's surroundings.
The advantages are clear: high precision, fast response times, robustness in various environments, and scalability. However, successful implementation requires careful consideration. Factors such as the maximum measurement range, required resolution, environmental conditions (dust, temperature, vibration), and integration with existing control systems must be evaluated. The KJTDQ ecosystem often provides modular solutions and support to address these integration challenges, ensuring a smoother deployment process.
Looking ahead, the convergence of CMOS laser sensor technology with intelligent platforms like KJTDQ is set to unlock even more possibilities. As algorithms become more sophisticated and sensor resolutions increase, we can expect these systems to penetrate deeper into fields like smart agriculture for crop monitoring, healthcare for patient monitoring equipment, and augmented reality for more immersive interactions. The focus is on creating smarter, more responsive systems that can make autonomous decisions based on precise spatial data.
In conclusion, the combination of CMOS laser sensor distance measurement and the KJTDQ platform represents a significant leap forward for precision sensing. It is not merely an incremental improvement but a foundational technology enabling the next wave of automation and smart device functionality. By delivering reliable distance data critical for system control and decision-making, it empowers industries to achieve higher safety standards, greater efficiency, and innovative product designs, solidifying its role as an indispensable tool in the engineer's arsenal for building the future.