Imagine a robotic arm assembling a smartphone with flawless accuracy, or a self-driving car navigating a crowded street without a hitch. At the heart of these marvels lies a silent hero: the photoelectric distance sensor. This unassuming device uses light to measure distances with incredible precision, transforming everything from factory floors to everyday gadgets. If you’ve ever pondered how machines “see” and respond to their surroundings, you’re about to uncover the science behind this groundbreaking technology. In this article, we’ll delve into how photoelectric sensors work, their diverse types, real-world applications, and why they’re revolutionizing industries worldwide. Forget clunky mechanical tools—this is non-contact measurement at its finest.
Photoelectric distance sensors operate on a simple yet ingenious principle: they emit a beam of light—often infrared—toward a target, and then analyze the reflected light to calculate distance. The core components include an emitter, which sends out the light, and a receiver, which detects the bounce-back. By measuring factors like the time of flight or the intensity of the return signal, these sensors provide rapid, accurate readings without physical contact. This non-invasive approach minimizes wear and error, making them ideal for environments where delicate or moving objects are involved. For instance, in reflective models, the receiver picks up light bounced off the target, while through-beam variants use a separate emitter and receiver for direct detection. This versatility allows photoelectric distance sensors to adapt to various scenarios, from detecting tiny components on a conveyor belt to gauging distances in harsh outdoor settings. Essentially, they turn light into data, enabling machines to interact intelligently with their world.

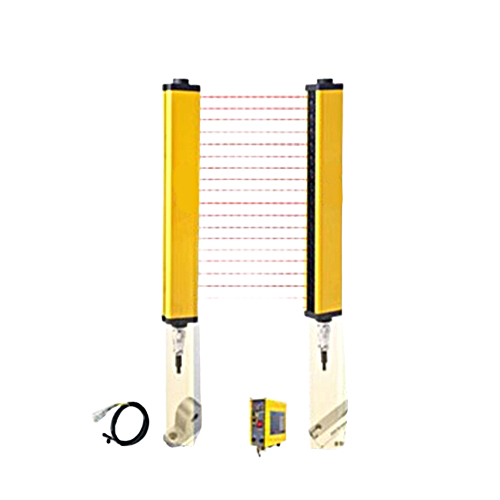
Now, let’s explore the main types of photoelectric sensors to understand their flexibility. The most common categories include diffused reflective sensors, retro-reflective sensors, and through-beam sensors. Diffused reflective types, such as those using infrared light, have both emitter and receiver in one unit. They’re perfect for close-range applications where the sensor and target are in proximity, like in packaging lines. Retro-reflective sensors, on the other hand, rely on a reflector to bounce light back, boosting range and reliability for mid-distance tasks, such as monitoring vehicle positions in automated car washes. Meanwhile, through-beam sensors feature separate emitter and receiver units, creating a “light curtain” that detects objects breaking the beam—ideal for long-range precision in robotics or security systems. Each type leverages the photoelectric effect, where photons interact with materials to generate electrical signals. This ensures consistent performance even in challenging conditions like fog or dust, highlighting why these sensors are a staple in modern automation.
When it comes to applications, photoelectric distance sensors shine across countless industries, offering unparalleled benefits. In industrial automation, they’re workhorses for quality control, ensuring products meet exact specs by measuring gaps, thicknesses, or alignments on assembly lines. Automotive sectors rely on them for collision avoidance systems, where sensors detect obstacles and trigger instant responses—crucial for enhancing road safety. Consumer electronics, too, benefit greatly; think of smartphones using proximity sensors to dim screens during calls. Even healthcare adopts them for precise positioning in medical devices, such as robotic surgery tools. The key advantage here is high accuracy with minimal calibration, reducing downtime and costs. These sensors excel in non-contact distance measurement, making them safer and more hygienic than tactile alternatives. Plus, they integrate seamlessly with IoT systems, providing real-time data for smarter decision-making in smart factories. This widespread utility underscores their role as enablers of innovation.
But what sets photoelectric sensors apart are their overwhelming advantages in efficiency and reliability. Unlike ultrasonic or mechanical sensors, they offer faster response times—often in milliseconds—ensuring processes run smoothly without delays. Their immunity to electromagnetic interference makes them robust in noisy environments, while the use of infrared light allows operation in darkness or varying lighting conditions. Cost-effectiveness is another standout feature, as durable designs translate to long lifespans and low maintenance. For businesses, this means higher productivity and reduced waste, a win-win in competitive markets. Moreover, advancements in technology have led to compact, energy-efficient models that fit into portable gadgets, expanding their reach to everyday users. By choosing the right photoelectric distance sensor, engineers unlock solutions that blend precision with practicality.
From transforming warehouses to powering the next wave of smart devices, photoelectric distance sensors are indispensable tools in our tech-driven era. They prove that light-based measurement isn’t just science fiction—it’s a reality driving progress. Whether you’re optimizing a production line or enhancing a personal project, understanding these sensors can illuminate new possibilities. So, next time you witness automation in action, remember the invisible light beams making it all possible.