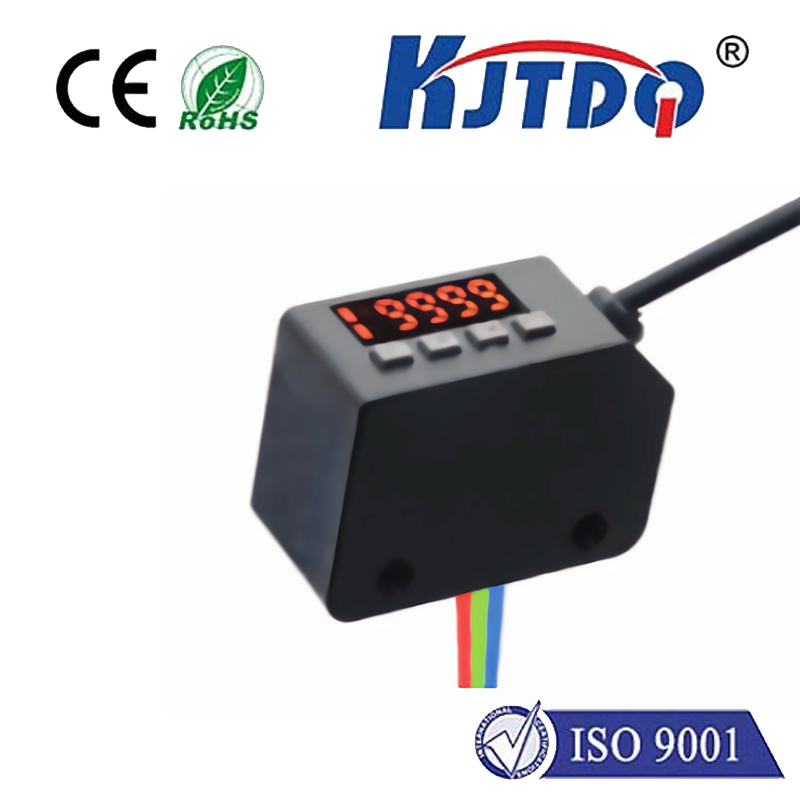
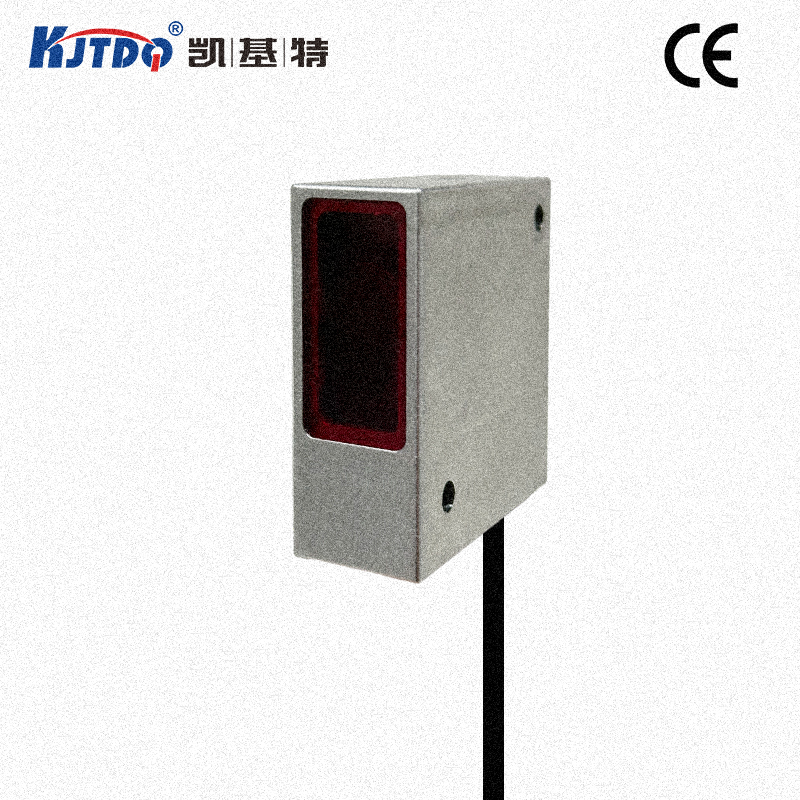
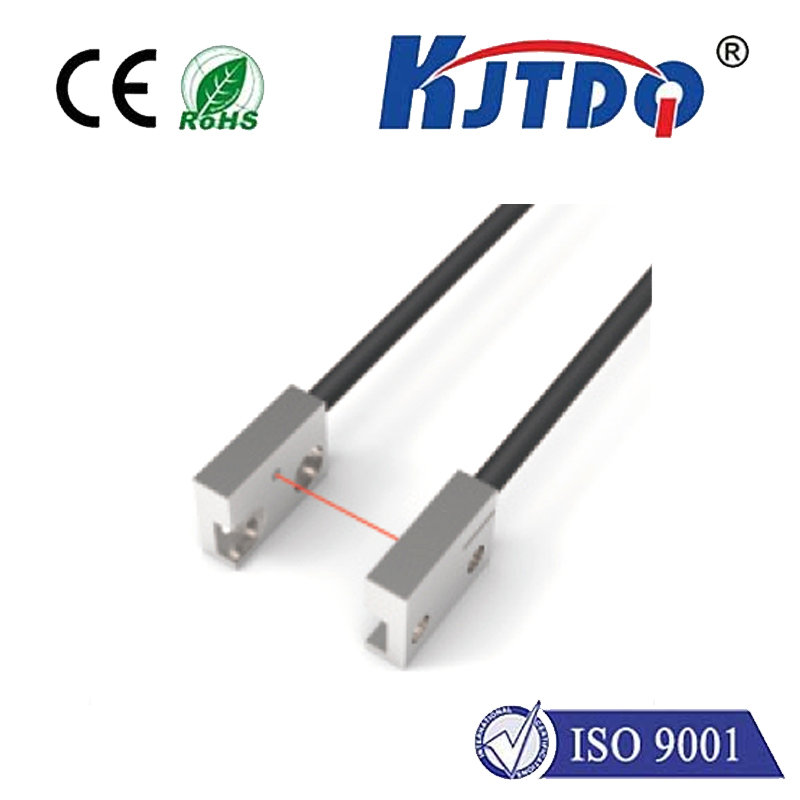
Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка
Unlocking Precision: The Power of Laser Grid Sensors in Modern Technology Imagine a world where machines can “see” with pinpoint accuracy, detecting objects, measuring distances, and mapping environments in real-time. This is no longer science fiction but a reality powered by laser grid sensors. These advanced devices are transforming industries, from robotics and autonomous vehicles to security and manufacturing. In this article, we’ll explore how laser grid sensors work, their applications, and why they are becoming indispensable in today’s technology-driven world.
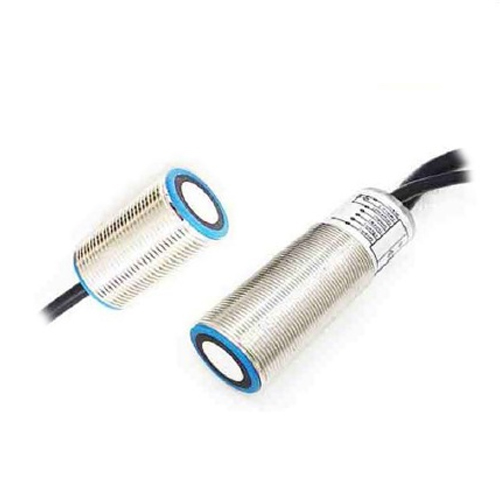
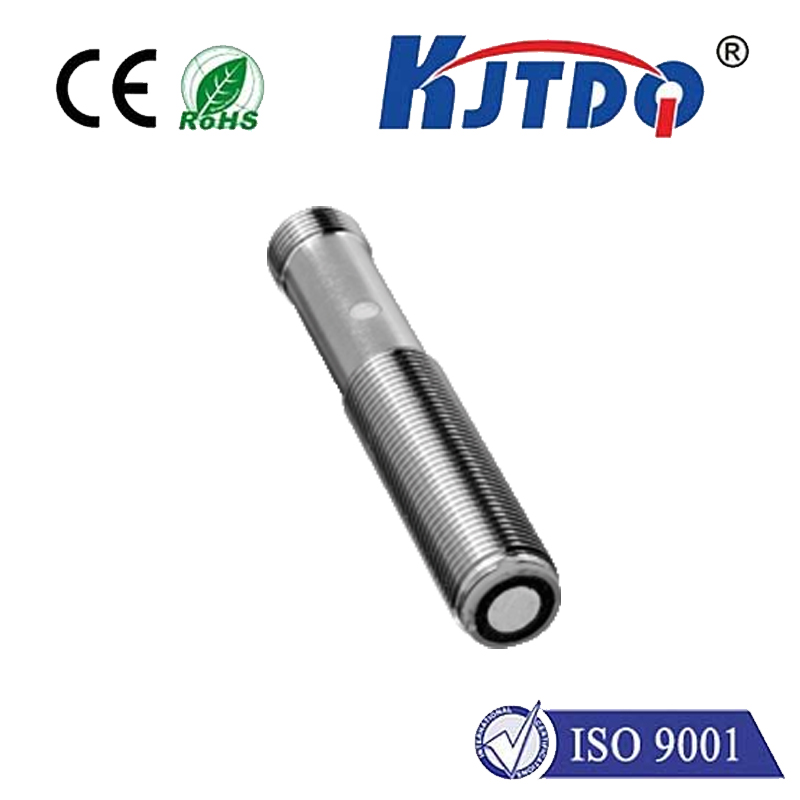
А.лазерный решёточный датчик is a sophisticated device that projects a grid of laser beams onto a surface or object. By analyzing the distortion or reflection of these beams, the sensor can capture detailed information about the object’s shape, size, and position. Think of it as a high-tech version of a flashlight casting a grid pattern on a wall, but with the ability to measure and interpret every detail. These sensors typically combine laser technology, cameras, and advanced algorithms to create 3D representations of their surroundings. The result is a highly accurate and real-time data stream that can be used for various applications.
The operation of a laser grid sensor can be broken down into three key steps:
Laser Projection: The sensor emits a grid of laser beams onto the target area. This grid can be visible or invisible, depending on the type of laser used.
Reflection Detection: The beams bounce off the surface of the object and return to the sensor. The sensor’s camera or photodetector captures these reflections.
Data Processing: Advanced algorithms analyze the distortions in the grid pattern caused by the object’s shape or movement. This data is then used to generate a 3D map or measurement. The precision of laser grid sensors lies in their ability to detect even the slightest changes in the grid pattern, making them ideal for applications that require micron-level accuracy.

The versatility of laser grid sensors has led to their adoption across a wide range of industries. Here are some of the most impactful applications:
In robotics, laser grid sensors are used for object detection, navigation, and precise manipulation. For example, robotic arms in manufacturing plants rely on these sensors to identify and pick up objects with incredible accuracy. Similarly, autonomous robots use them to map their environment and avoid obstacles.
Self-driving cars depend on laser grid sensors, often integrated into LiDAR systems, to create real-time 3D maps of their surroundings. These maps help the vehicle detect pedestrians, other cars, and road conditions, ensuring safe and efficient navigation.
Laser grid sensors are also used in security systems to detect intrusions. By projecting an invisible grid across a protected area, these sensors can detect any movement or disturbance, triggering an alarm or alert.
In healthcare, laser grid sensors are used in advanced imaging systems to create detailed 3D models of organs, bones, or tissues. This technology is particularly useful in surgeries, where precision is critical.
AR and VR systems use laser grid sensors to track the user’s movements and map the physical environment. This enables immersive experiences where virtual objects interact seamlessly with the real world.
The growing popularity of laser grid sensors can be attributed to their numerous advantages:
Высокая точность: These sensors can detect objects and measure distances with sub-millimeter accuracy.
Данные в реальном времени: They provide instant feedback, making them ideal for dynamic applications like robotics and autonomous vehicles.
Non-Contact Measurement: Laser grid sensors can measure objects without physical contact, reducing the risk of damage or contamination.
Многогранный.: They can be used in a wide range of environments, from industrial settings to outdoor spaces.
Despite their many benefits, laser grid sensors are not without challenges. One major limitation is their sensitivity to environmental factors like dust, fog, or bright sunlight, which can interfere with the laser beams. Additionally, high-end sensors can be expensive, limiting their accessibility for some applications. However, ongoing research and development are addressing these issues. Innovations in miniaturization, cost reduction, and environmental robustness are making laser grid sensors more practical and affordable. For example, advancements in solid-state LiDAR technology are paving the way for smaller, more durable sensors that can operate in harsh conditions.
As technology continues to evolve, the demand for precise, real-time data will only grow. Laser grid sensors are at the forefront of this trend, enabling machines to interact with their environment in ways that were once unimaginable. From enhancing the safety of autonomous vehicles to revolutionizing healthcare, these sensors are shaping the future of multiple industries. Their ability to combine accuracy, speed, and versatility makes them a cornerstone of modern technology. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, an industry professional, or simply curious about the latest innovations, laser grid sensors are a topic worth exploring.