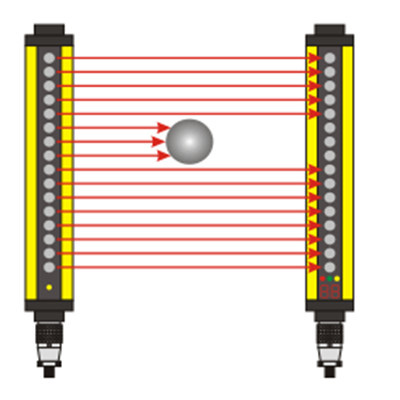
Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка
Imagine a technology that captures microscopic surface details with laser-sharp accuracy, powers quality control in manufacturing, and even enables 3D facial recognition. This is the power of Лазерная триангуляция—a non-contact sensing method revolutionizing industries from aerospace to healthcare. In this article, we explore how this cutting-edge technique works, its real-world applications, and why it’s becoming indispensable in the era of smart manufacturing and automation.
At its core, Лазерная триангуляция relies on geometry and optics to calculate distances with exceptional precision. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
Why has this method become a gold standard for non-contact measurement? Let’s break down its strengths:
The versatility of Лазерная триангуляция has made it a cornerstone of modern engineering and research. Below are standout use cases:
In manufacturing, even minor deviations can lead to product failures. Laser triangulation systems are deployed to:
Monitor assembly line components for dimensional accuracy.
Detect surface defects like scratches or dents in real time.

Measure thickness coatings in semiconductor production. For example, in electronics manufacturing, these systems verify the flatness of circuit boards, preventing costly soldering errors.
From prosthetics to surgical tools, precision is non-negotiable in healthcare. Laser triangulation aids in:
Creating custom-fit orthopedic implants using 3D scans of patient anatomy.
Measuring microscopic wear on medical devices during R&D.
Analyzing skin topography for dermatological research.
Autonomous robots rely on accurate environmental mapping. Laser triangulation sensors enable:
Obstacle detection and navigation in dynamic environments.
Bin-picking systems that identify and grasp irregularly shaped objects.
Agricultural robots that monitor crop health by scanning plant surfaces.
Museums and archaeologists use this technology to digitize artifacts without physical contact. Scans reveal hidden cracks, erosion patterns, and even ancient tool marks invisible to the naked eye.
While powerful, laser triangulation isn’t without constraints. Key considerations include:
As industries demand faster, smaller, and smarter solutions, laser triangulation technology is evolving in exciting ways:
From factory floors to operating rooms, Лазерная триангуляция continues to push the boundaries of what’s measurable. Its blend of speed, precision, and adaptability ensures it will remain a vital tool as industries embrace automation and data-driven decision-making. Whether optimizing production lines or preserving history, this technology proves that sometimes, the simplest geometric principles yield the most groundbreaking solutions.