Laser RPM Sensors: Precision Measurement for Modern Industrial Applications In an era where industrial automation and precision engineering dominate, the ability to measure rotational speed with flawless accuracy has become a cornerstone of efficiency. Enter the laser RPM sensor—a cutting-edge tool revolutionizing how industries monitor and optimize rotating machinery. From automotive diagnostics to aerospace manufacturing, these sensors are quietly transforming workflows, reducing downtime, and enhancing safety. But what exactly makes laser RPM sensors indispensable in today’s tech-driven world? Let’s dive into their mechanics, applications, and why they’re a game-changer for engineers and technicians alike.
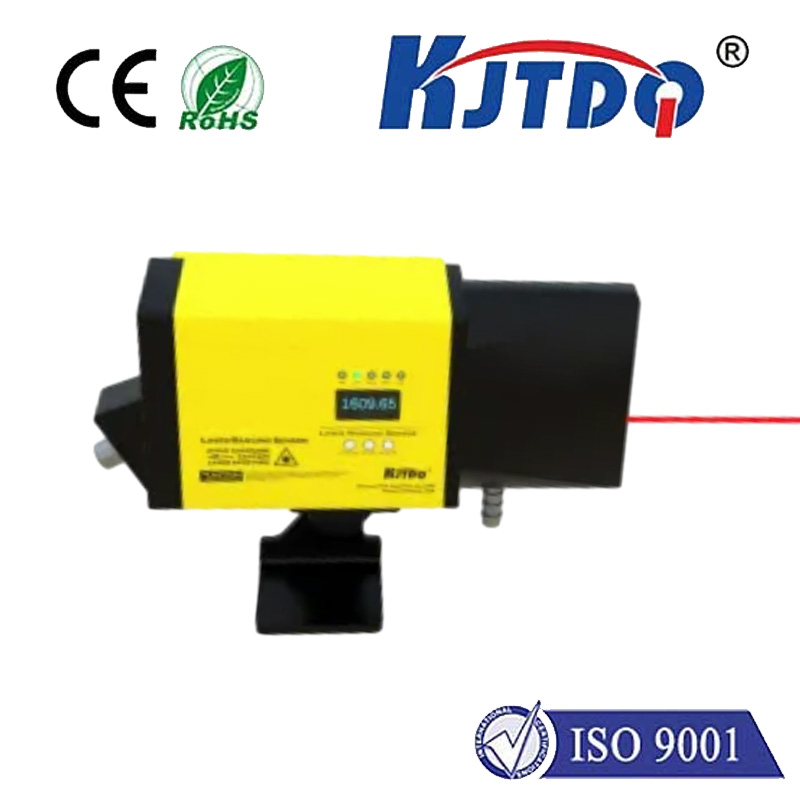
At their core, laser RPM sensors operate on a simple yet ingenious principle: non-contact measurement. Unlike traditional mechanical tachometers that require physical contact with rotating components, laser sensors use focused light beams to detect rotational speed. Here’s a breakdown of their functionality:
The versatility of laser RPM sensors makes them invaluable across industries. Below are some standout use cases:
In vehicle testing labs, these sensors monitor engine crankshafts, turbochargers, and wheel speeds. Their non-invasive nature allows engineers to gather data without disrupting delicate systems. For example, during dyno testing, a laser sensor can track RPM fluctuations in real time, helping optimize fuel efficiency and emission controls.

Turbine blades in jet engines spin at dizzying speeds—often exceeding 10,000 RPM. Laser-based sensors provide critical data for maintenance crews, ensuring blades operate within safe limits. Their ability to function in extreme temperatures and vibrations makes them ideal for aviation’s rigorous demands.
Conveyor belts, CNC machines, and robotic arms rely on precise rotational control. By integrating laser RPM sensors, factories minimize production errors caused by speed mismatches. A packaging line, for instance, can use these sensors to synchronize robotic arms with conveyor speeds, reducing waste and downtime.
Wind turbines depend on consistent blade rotation to generate power efficiently. Laser sensors monitor blade RPM, alerting operators to imbalances or wear before catastrophic failures occur. This proactive approach is vital for maintaining renewable energy infrastructure.
Why are industries rapidly adopting laser RPM sensors? Here’s how they outperform conventional methods:
Not all laser RPM sensors are created equal. To select the ideal model for your needs, consider these factors:
As industries push toward Industry 4.0 and IoT integration, laser RPM sensors are evolving to meet smarter demands. Innovations on the horizon include:
From automotive workshops to wind farms, the laser RPM sensor has proven its worth as a silent guardian of precision and productivity. By marrying cutting-edge optics with rugged engineering, this technology continues to redefine what’s possible in rotational speed measurement—one laser pulse at a time.