Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка
Unlocking the Potential of Inductive Proximity Sensors in Modern Automation In the rapidly evolving world of industrial automation, inductive proximity sensors have emerged as a cornerstone technology. These devices, which detect the presence of metallic objects without physical contact, are transforming how industries approach efficiency, safety, and precision. Whether you’re in manufacturing, automotive, or robotics, understanding the capabilities and applications of inductive proximity sensors can significantly enhance your operational processes.
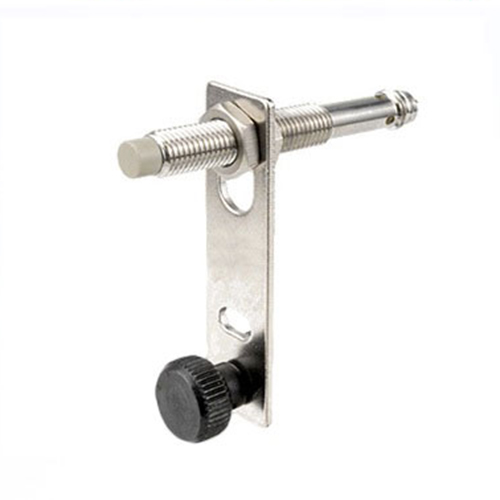
At their core, inductive proximity sensors are non-contact devices that use electromagnetic fields to detect metallic objects. Unlike other types of sensors that rely on physical contact or optical mechanisms, these sensors operate purely on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When a metallic object enters the sensor’s field, it induces eddy currents, which alter the sensor’s electromagnetic field. This change is then detected and converted into an electrical signal, alerting the system to the object’s presence.

One of the standout features of inductive proximity sensors is their robustness. Designed to withstand harsh industrial environments, these sensors are resistant to dust, dirt, and moisture, making them ideal for use in challenging conditions. Additionally, their non-contact nature means there’s no wear and tear from physical interaction, ensuring a longer lifespan and reduced maintenance costs. Another significant advantage is their high-speed detection capabilities. In industries where milliseconds matter, such as automotive assembly lines, inductive proximity sensors provide instantaneous feedback, enabling faster and more precise operations. Their ability to detect a wide range of metallic materials, from steel to aluminum, further enhances their versatility.
The applications of inductive proximity sensors are vast and varied. In the manufacturing sector, they are commonly used for position sensing, object detection, and quality control. For instance, in a production line, these sensors can ensure that components are correctly positioned before assembly, reducing errors and improving efficiency. In the automotive industry, inductive proximity sensors play a critical role in assembly lines, where they monitor the position of parts and ensure precise alignment. They are also used in safety systems, such as detecting the presence of metallic objects in hazardous areas, preventing accidents before they occur. The robotics industry benefits greatly from these sensors as well. Robots equipped with inductive proximity sensors can navigate their environment more effectively, avoiding collisions and interacting with metallic objects with precision. This capability is particularly valuable in applications such as pick-and-place operations and automated guided vehicles (AGVs).
When selecting an inductive proximity sensor, several factors should be considered. The sensing range is crucial, as it determines how close an object needs to be for detection. Additionally, the Частота работы affects the sensor’s response time and suitability for specific applications. For high-speed operations, a sensor with a higher frequency is typically preferred. The housing material is another important consideration. Sensors housed in stainless steel or nickel-plated brass are more durable and better suited for harsh environments, while plastic housings are lighter and more cost-effective for less demanding applications.
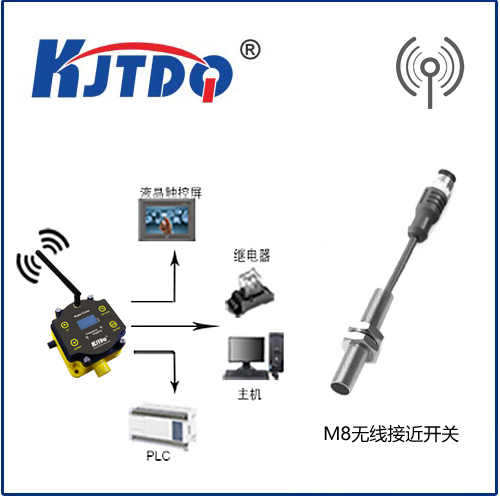
As automation continues to advance, so too does the technology behind inductive proximity sensors. Innovations such as smart sensors equipped with IoT capabilities are becoming increasingly popular. These sensors can communicate with other devices in a network, providing real-time data and enabling predictive maintenance. This not only reduces downtime but also optimizes operational efficiency. Another emerging trend is the development of miniaturized sensors. As industries demand more compact and lightweight solutions, manufacturers are creating smaller sensors without compromising on performance. These miniaturized sensors are particularly valuable in applications where space is limited, such as in wearable devices or small-scale robotics.
Inductive proximity sensors have proven to be indispensable in modern automation, offering unmatched reliability, speed, and versatility. By understanding their features, applications, and the factors to consider when choosing one, industries can harness their full potential to drive efficiency and innovation. Whether you’re looking to enhance your manufacturing processes, improve safety in your automotive operations, or optimize your robotics systems, these sensors are a powerful tool to have in your arsenal.