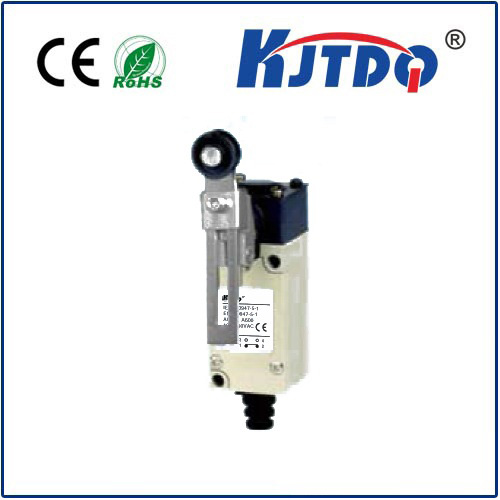
Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка
In the realm of precision measurement, the accurate laser rangefinder sensor stands as a cornerstone technology, revolutionizing how distances are captured across countless industries. Unlike traditional measuring tapes or ultrasonic sensors, these devices harness the speed and coherence of light to deliver unparalleled accuracy and reliability. The core principle is elegantly simple: the sensor emits a focused laser pulse towards a target, measures the time it takes for the pulse to reflect back, and calculates the distance with extreme precision. This Time-of-Flight (ToF) method, often enhanced by phase-shift analysis for even finer resolution, is what empowers these sensors to achieve millimeter-level accuracy even over substantial ranges.
The applications for accurate laser rangefinder sensors are vast and transformative. In construction and civil engineering, they are indispensable for land surveying, building layout, and volume calculations, drastically reducing human error and project timelines. The forestry industry relies on them for efficient timber inventory management. In the automotive sector, they form the critical "eyes" of Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS), enabling features like adaptive cruise control and collision avoidance by accurately gauging the distance to vehicles and obstacles. Furthermore, they are integral to robotics for navigation and object manipulation, in sports for tracking performance, and in logistics for warehouse automation and inventory management.
When selecting an accurate laser rangefinder sensor, several key specifications demand attention. Range and accuracy are the primary metrics; a sensor must cover the required working distance while maintaining the necessary precision for the task. Measurement speed and update rate are crucial for dynamic applications like autonomous vehicles or high-speed automation. The laser class (typically Class 1 or Class 2 for eye safety) and ingress protection (IP) rating determine the sensor's durability and suitability for harsh outdoor or industrial environments. Connectivity options, such as USB, Ethernet, or various industrial fieldbuses, ensure seamless integration into existing systems.
Modern advancements continue to push the boundaries of what's possible. The integration of sophisticated digital signal processing (DSP) chips filters out ambient light noise and improves performance in challenging conditions. Some sensors now incorporate Bluetooth or Wi-Fi for wireless data transfer and configuration. The miniaturization of components has led to more compact, robust, and power-efficient designs, opening doors for use in portable devices and drones. Looking ahead, the convergence of laser ranging data with other sensor inputs like inertial measurement units (IMUs) and cameras is paving the way for even more intelligent and context-aware systems.
For businesses and engineers, implementing an accurate laser rangefinder sensor is a strategic investment in efficiency, quality, and safety. It eliminates guesswork, automates tedious manual processes, and provides reliable data for critical decision-making. Whether it's ensuring the precise placement of a structural beam, guiding an autonomous mobile robot through a factory floor, or making driving safer, this technology delivers tangible value. The KJTDQ series, representing the latest in this field, exemplifies these qualities with its robust design, high update rates, and exceptional accuracy, making it a preferred choice for demanding professional applications where every millimeter counts.