In the rapidly evolving landscape of industrial automation, precision, reliability, and efficiency are non-negotiable. At the heart of countless automated systems, from intricate assembly lines to robust material handling equipment, lies a critical component: the proximity sensor. Among the various types available, the E2E series proximity sensor has emerged as a benchmark for performance and durability. This guide delves into the technology, applications, and distinct advantages of these sensors, illustrating why they are indispensable in modern manufacturing and beyond.
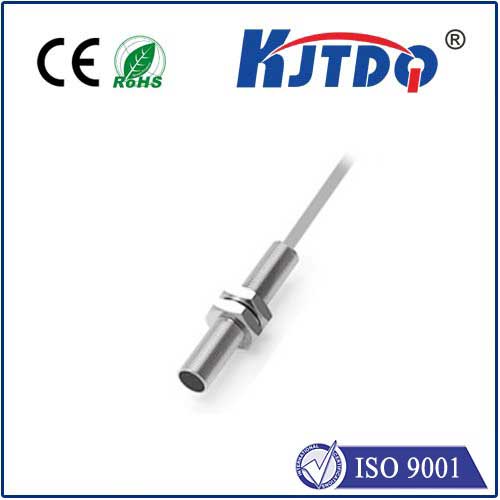
Proximity sensors are devices that detect the presence or absence of an object without physical contact. They achieve this by emitting an electromagnetic field or a beam of electromagnetic radiation and looking for changes in the field or return signal. The E2E series represents a specific, highly regarded line of cylindrical inductive proximity sensors. Inductive sensors are specifically designed to detect metallic objects. Their core principle involves an oscillator circuit that generates a high-frequency electromagnetic field at the sensing face. When a metallic target enters this field, it induces eddy currents within the target, which in turn dampens the oscillator's oscillations. This damping is detected by the sensor's circuitry, triggering a solid-state output switch.
The "E2E" designation typically refers to a standardized form factor and performance profile, often associated with major manufacturers in the automation sector. These sensors are characterized by their cylindrical metal housing, offering exceptional resilience in harsh industrial environments. They are built to withstand exposure to oils, coolants, dust, and mechanical impacts, ensuring consistent operation where other components might fail. Key specifications include various sensing distances (ranging from a few millimeters to several centimeters), different output types (like NPN or PNP transistor outputs), and housing materials such as nickel-plated brass or stainless steel, which provide superior resistance to corrosion.
The applications for E2E series proximity sensors are vast and varied. In automotive manufacturing, they are crucial for part positioning, robotic arm end-effector verification, and conveyor line control, ensuring engines and components are assembled with millimeter precision. In packaging machinery, these sensors detect the presence of metal lids, cans, or foil seals, synchronizing filling and capping operations. They play a vital role in material handling by counting metal parts, monitoring pallet positions, and providing end-of-travel limits for automated guided vehicles (AGVs). Furthermore, in metalworking and CNC machining centers, E2E sensors are used for tool breakage detection, workpiece positioning, and door interlocking for safety.
What truly sets the E2E series apart are its engineered advantages. First is its exceptional reliability. The non-contact sensing principle eliminates mechanical wear and tear associated with limit switches, leading to a dramatically longer operational lifespan and reduced maintenance costs. Second is its high-speed response. These sensors can detect objects at incredibly fast rates, making them suitable for high-speed production lines where every millisecond counts. Third is environmental robustness. Sealed to high ingress protection (IP) ratings like IP67 or IP69K, they are resistant to water, steam, and high-pressure washdowns, common in food and beverage or pharmaceutical industries. Finally, their simplicity of installation and setup, often featuring LED status indicators for easy diagnostics, minimizes downtime during integration or troubleshooting.
When selecting an E2E series sensor for a specific task, several factors must be considered. The sensing distance, often specified as the "nominal sensing distance" (Sn), must be chosen with a safety margin to account for target material, size, and temperature variations. The target material itself is critical; while inductive sensors detect metals, different metals like steel, aluminum, or copper have different damping effects, which can influence the effective sensing range. The sensor's housing diameter and thread size (e.g., M8, M12, M18, M30) must match the mounting hole. Environmental conditions such as ambient temperature, presence of strong magnetic fields, or conductive dust also guide the selection of the appropriate sensor variant.
Looking ahead, the integration of E2E series proximity sensors with Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) platforms represents the next frontier. Smart sensors with integrated IO-Link communication can provide not just a simple on/off signal but a wealth of diagnostic data, including operating temperature, signal strength, and potential contamination warnings. This enables predictive maintenance strategies, where a sensor can alert operators to potential issues before they cause unplanned downtime, further elevating plant efficiency and operational intelligence.
In conclusion, the E2E series proximity sensor is far more than a simple switch. It is a foundational element of modern industrial automation, enabling the precise, reliable, and contactless detection that complex automated systems depend on. Its rugged design, consistent performance, and adaptability across countless applications make it a trusted choice for engineers and system integrators worldwide. As industries continue to push the boundaries of productivity and smart manufacturing, the role of these robust and reliable sensors will only become more central, silently ensuring that the wheels of industry continue to turn smoothly and efficiently.