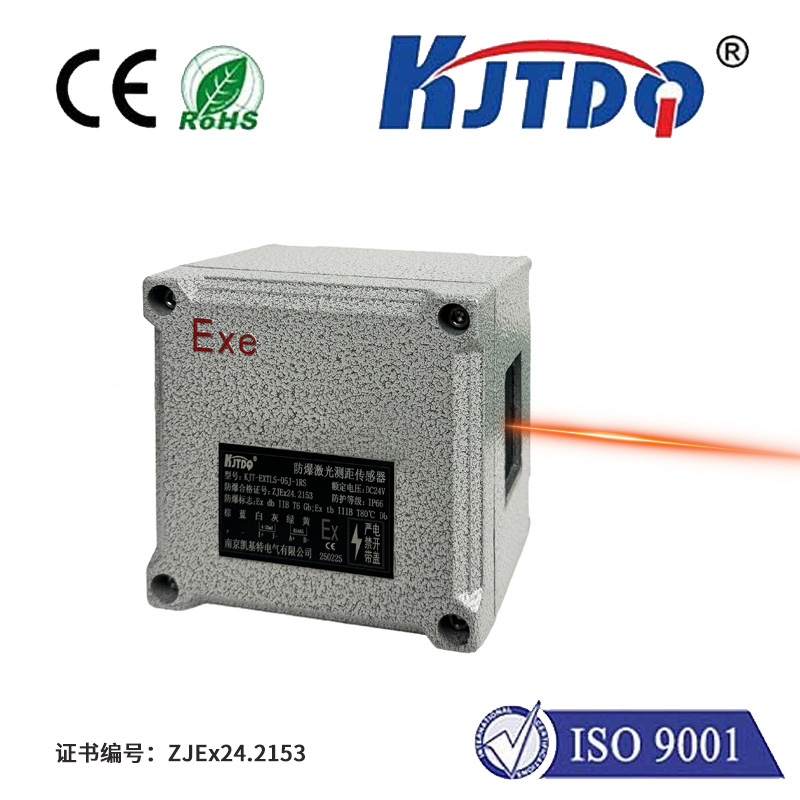
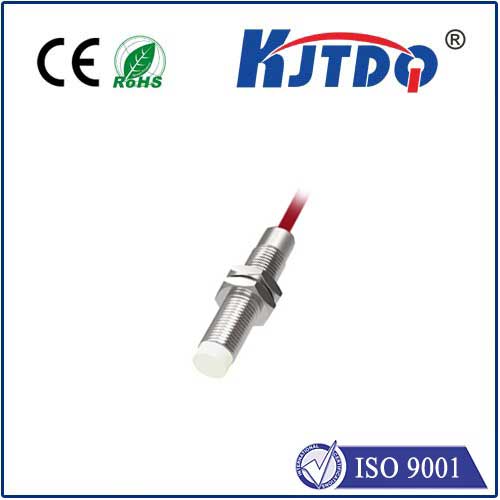
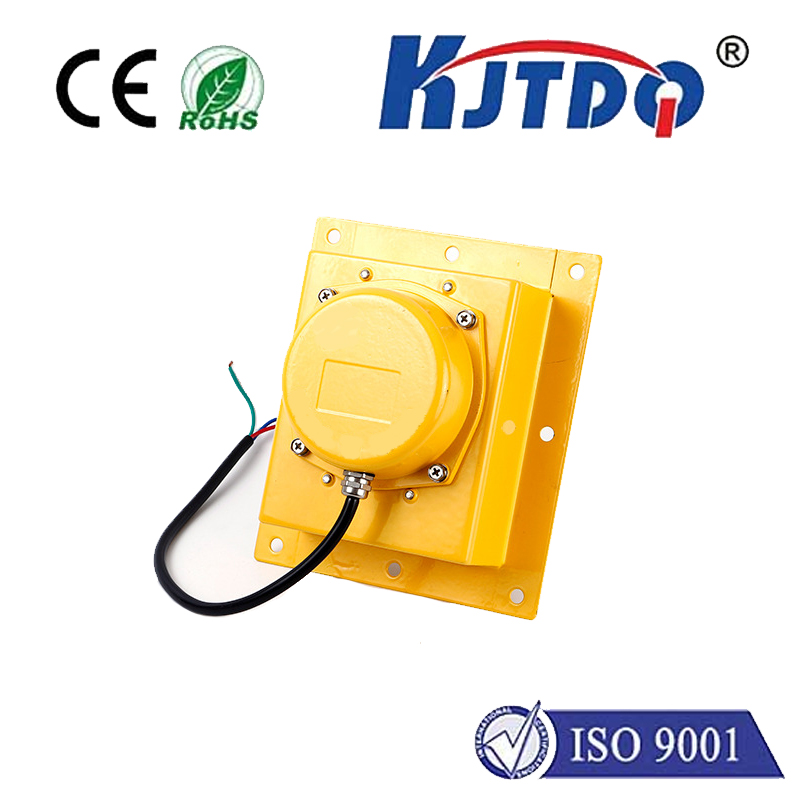
Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка
In today's fast-paced technological landscape, the demand for accurate and reliable detection systems has never been higher. Among the various solutions available, radar proximity sensors stand out as a cornerstone of modern automation and safety applications. These sensors utilize radio waves to detect the presence, distance, and speed of objects without physical contact, making them indispensable in industries ranging from automotive to industrial manufacturing.
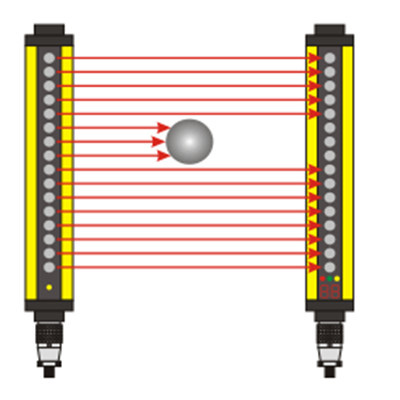
Radar proximity sensors operate on the principle of emitting high-frequency radio waves and analyzing the reflected signals. When these waves encounter an object, they bounce back to the sensor, which then calculates the time taken for the round trip. This data is processed to determine the object's proximity with remarkable precision. Unlike traditional infrared or ultrasonic sensors, radar sensors are less affected by environmental factors such as dust, fog, or temperature fluctuations, ensuring consistent performance in challenging conditions.
One of the key advantages of radar proximity sensors is their versatility. In the automotive sector, they are integral to advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), enabling features like adaptive cruise control, blind-spot detection, and collision avoidance. By providing real-time data on nearby vehicles and obstacles, these sensors enhance road safety and pave the way for autonomous driving technologies. Similarly, in industrial settings, radar sensors monitor machinery movements, manage inventory in warehouses, and safeguard workers by detecting intrusions in hazardous zones.
The evolution of radar technology has led to the development of compact, cost-effective sensors suitable for consumer electronics and smart home devices. For instance, smart lighting systems use radar proximity sensors to detect human presence, automatically turning lights on or off to conserve energy. In healthcare, these sensors assist in patient monitoring, tracking vital signs without direct contact, which is especially valuable in infection control scenarios.
When selecting a radar proximity sensor, several factors come into play. Frequency range is critical; higher frequencies like 24 GHz or 77 GHz offer finer resolution for detailed detection, while lower frequencies provide longer range. Power consumption, size, and integration capabilities also influence the choice, depending on the application. Modern sensors often incorporate digital signal processing (DSP) and machine learning algorithms to filter noise and improve accuracy, adapting to dynamic environments seamlessly.
Despite their benefits, radar proximity sensors face challenges such as signal interference in crowded electromagnetic spectrums and limitations in detecting very small or non-metallic objects. However, ongoing research focuses on enhancing sensitivity and reducing false alarms through advanced modulation techniques and multi-sensor fusion. As the Internet of Things (IoT) expands, radar sensors are poised to become even more ubiquitous, connecting with networks to enable smarter, data-driven decisions.
In conclusion, radar proximity sensors represent a transformative technology that bridges the gap between automation and real-world interaction. Their ability to deliver precise, non-contact detection across diverse applications underscores their importance in driving innovation. Whether optimizing industrial efficiency or enhancing daily convenience, these sensors continue to redefine the boundaries of what is possible, making our world safer and more connected.