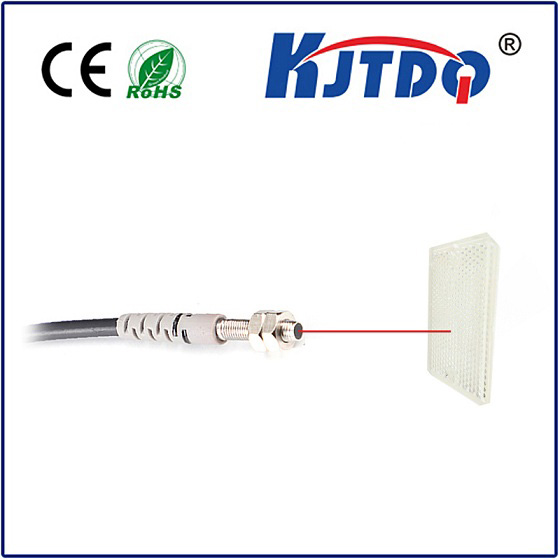
Проверка
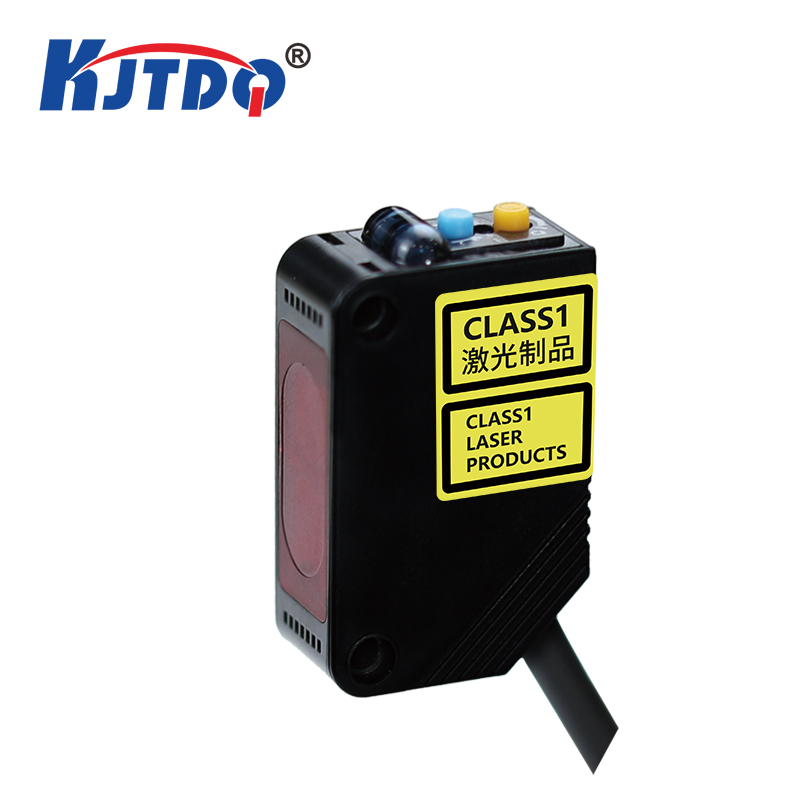
Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка

Проверка
Title: Linear Actuators with Limit Switches: An Overview
Linear actuators are a fundamental component in robotics, automation, and motion control systems. They convert linear force or torque into continuous movement along a linear path. In this article, we will explore the concept of linear actuators and their role in motion control systems, with a focus on limit switches.
1. Introduction to Linear Actuators
A linear actuator is a mechanical device that generates linear motion by applying a force or torque. It consists of a shaft, a piston or cylinder, and a mechanism to move the shaft along its length. Linear actuators are widely used in various applications, such as robotics, aerospace, automotive industry, and medical devices.
One of the key features of linear actuators is their ability to provide precise and repeatable motion control. This is due to their simplicity, low cost, and easy integration with other components. Linear actuators can be classified into different types based on their design characteristics, including:
* Push-pull linear actuators: These actuators use two opposing forces to move the shaft in either direction. The force applied to one side of the piston or cylinder pushes it forward, while the force applied to the opposite side pulls it backward.
* Revolving linear actuators: These actuators have a circular cross-section and rotate along an axis perpendicular to the linear motion. They are commonly used in applications where precise positioning and rotation are required.
* Rotary linear actuators: These actuators also have a circular cross-section but move along an axis parallel to the linear motion. They are often used in applications where high speed and torque are required, such as in wind turbines and electric motors.
1. Role of Limit Switches in Linear Actuators
Limit switches are electronic components that detect when a linear actuator has reached its end position or started moving again after being stopped. They play a crucial role in ensuring safe and reliable operation of linear actuators in motion control systems. When the linear actuator reaches its limit switch, the system automatically stops the motor or adjusts the position of the actuator to prevent damage to the machine or operator.
There are several types of limit switches available for linear actuators, including:
* Mechanical limit switches: These switches use mechanical contacts to indicate when the linear actuator has reached its end position or started moving again. They are simple and inexpensive but may generate noise and wear out over time.
* Optical limit switches: These switches use light signals to detect when the linear actuator has reached its end position or started moving again. They offer high accuracy and durability but are more expensive than mechanical switches.
* Microswitches: These switches are small and lightweight, making them suitable for use in compact motion control systems. They offer fast response times and reliable operation but may be prone to errors caused by environmental factors such as dust and humidity.
In summary, linear actuators with limit switches are an essential component of motion control systems that provide precise and repeatable motion control. By detecting when the linear actuator has reached its end position or started moving again, limit switches ensure safe and reliable operation of machines and prevent damage to operators.









