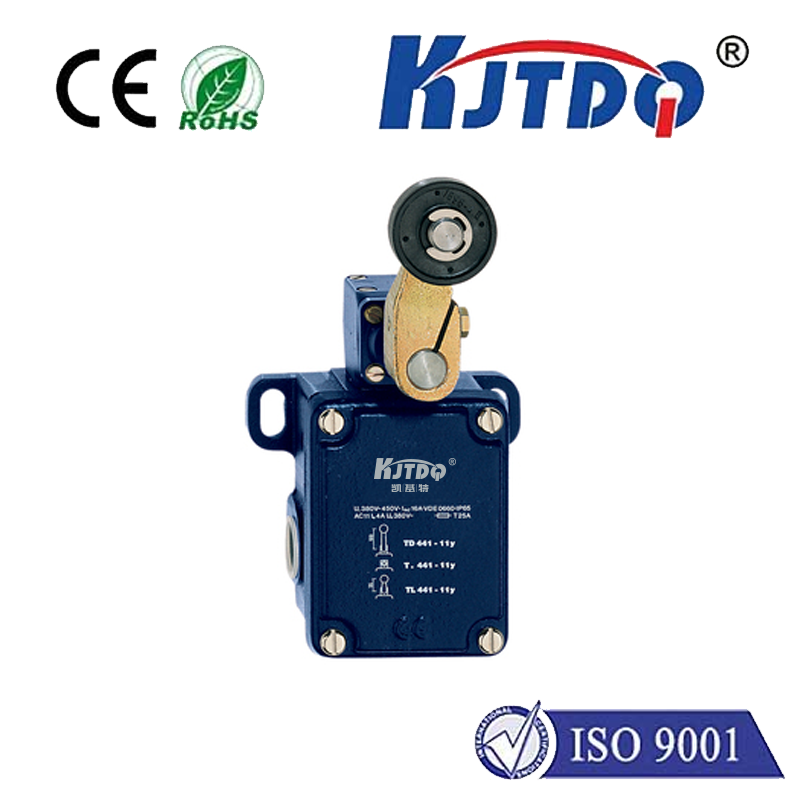
ограничитель поворота крана
- time:2025-08-04 12:54:39
- Нажмите:0
The Crane Rotary Limit Switch: Your Essential Guide to Safe and Efficient Lifting Operations
Imagine a massive crane hoisting a critical load high above a construction site or bustling factory floor. Now, envision that load swinging wildly beyond its intended path – a scenario packed with potential for catastrophic damage, injury, and costly downtime. Preventing this nightmare is the vital, often unseen, role of the ограничитель поворота крана. Far more than a simple component, this device stands as a fundamental guardian of safety and precision in the demanding world of material handling. Understanding its function, importance, and correct application is paramount for anyone involved in crane operations, maintenance, or procurement.
What Exactly is a Crane Rotary Limit Switch?
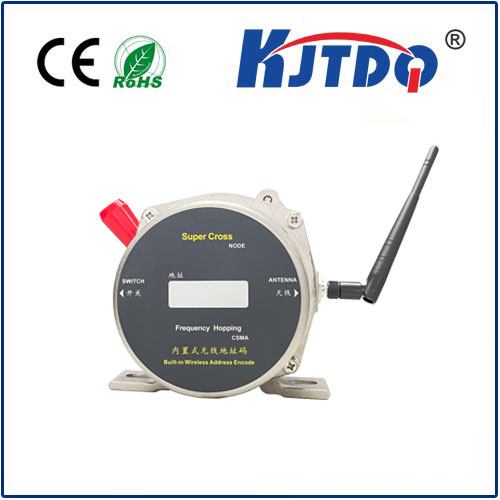
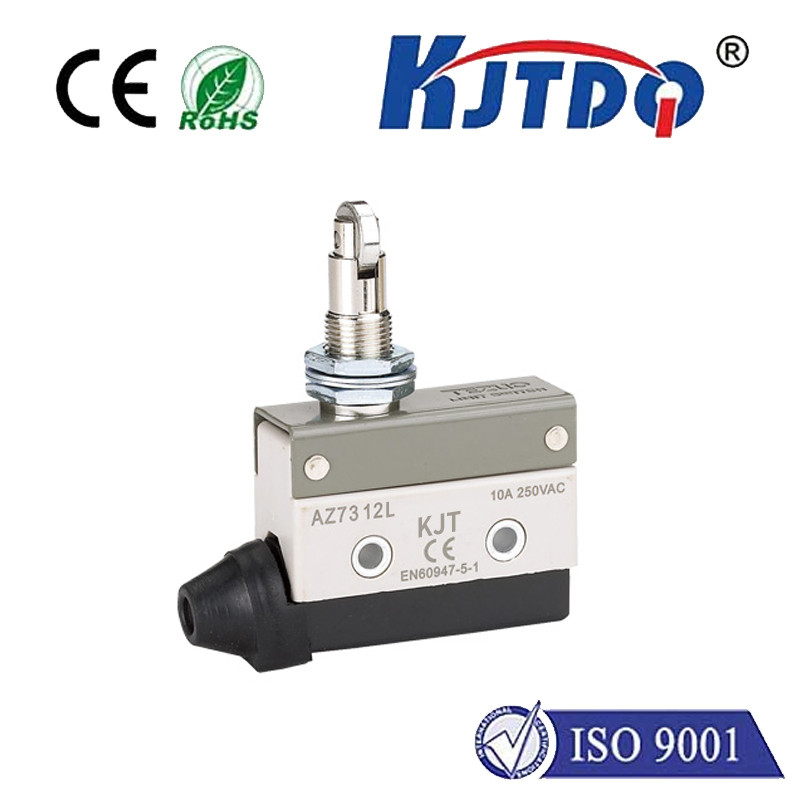
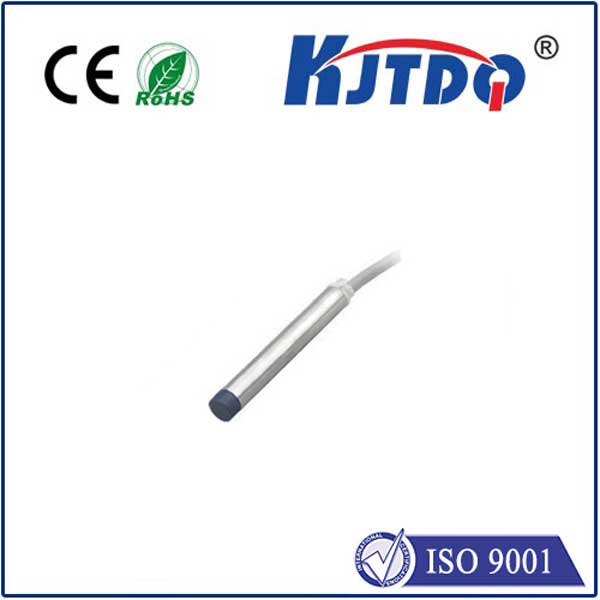
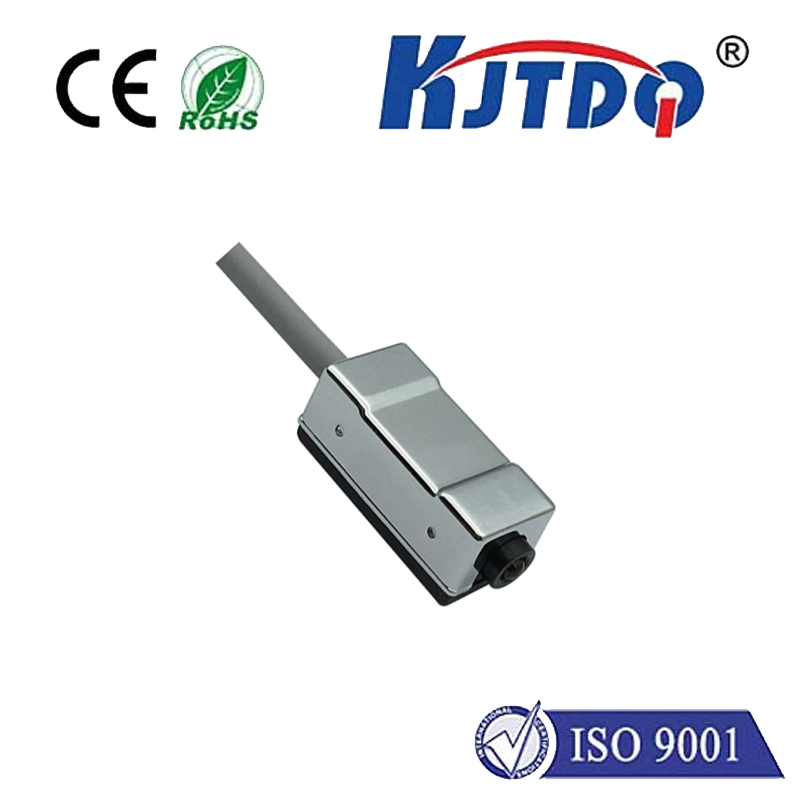
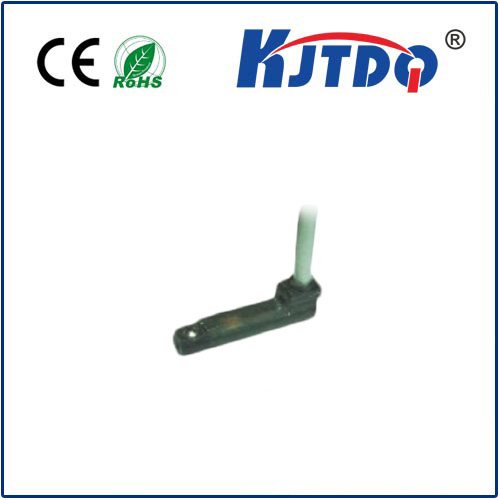
At its core, a crane rotary limit switch, also commonly called a ограничитель поворотного кулачка or crane rotation limiter, is a robust electro-mechanical safety device. Its primary mission is to monitor and control the rotational movement of a crane structure – most frequently the upper structure (slewing) of a tower crane or the boom rotation on certain mobile or overhead cranes. Unlike linear limit switches that detect straight-line movement, the ограничитель вращения is specifically engineered to track angular displacement, providing critical feedback on how far the crane has turned.
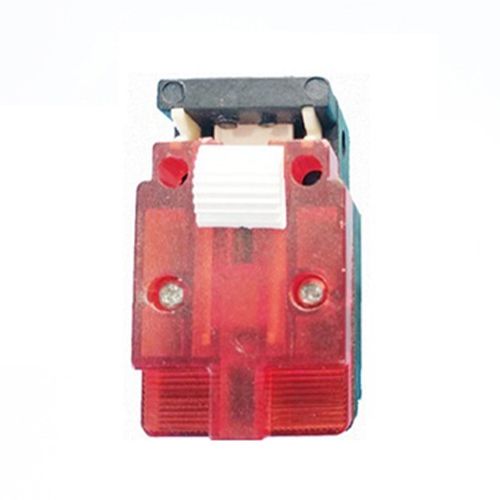
How Does This Critical Safety Device Work? Its operation is elegantly mechanical yet highly reliable. The switch body is typically securely mounted onto the crane’s fixed structure (like the tower or base). A rotating shaft extends from the switch and connects directly to the rotating part of the crane (the upper works or boom). As the crane rotates, this shaft turns proportionally inside the switch housing. Inside the housing, the shaft drives a series of precisely positioned cams. These cams, as they rotate, physically actuate rugged microswitches housed within the unit. Activating a microswitch either opens or closes an electrical circuit, sending a definitive signal to the crane’s control system. Think of it as a mechanical sentinel constantly reporting the crane’s angular position.

Why the Crane Rotary Limit Switch is Non-Negotiable for Safety
The significance of integrating a properly functioning rotary limit switch into a crane’s safety system cannot be overstated. Its primary functions deliver critical safeguards:
- Prevents Over-Travel (Slew Limiting): This is its most crucial safety role. The switch is configured to trigger at predetermined maximum clockwise and counter-clockwise rotation angles. When the crane reaches these extreme positions, the switch activates, cutting power to the slewing motor and preventing the structure from rotating further. This eliminates the risk of the crane colliding with structures, other cranes, power lines, or exceeding safe operational envelopes defined by site constraints or load charts.
- Defines Safe Working Zones: Beyond just absolute limits, multiple cams and switches within a single unit allow operators to set intermediate stopping points. This enables the creation of programmed safe working quadrants or exclusion zones, further enhancing operational safety during complex lifts or in congested environments.
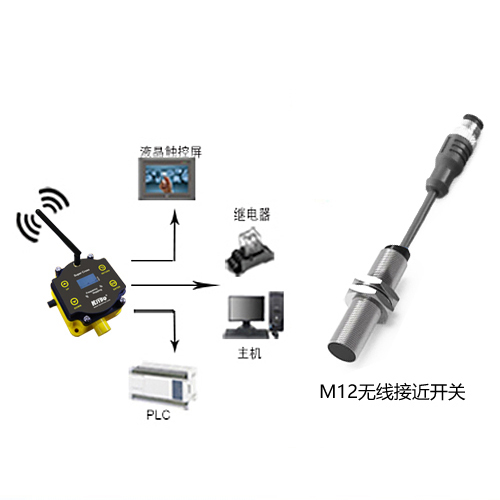
- Position Indication (Optional): Some more sophisticated rotary limit switches incorporate encoders or potentiometers alongside the switching mechanism. This provides continuous feedback on the crane’s exact rotational bearing, which can be displayed in the operator’s cab or fed into a control system for automated positioning functions.
Key Advantages Driving Their Ubiquitous Use in Crane Systems
Rotary limit switches remain the dominant solution for slew limiting despite advancements in sensor technology, and for compelling reasons:
- Proven Reliability: Their robust mechanical design, using high-grade materials for cams and switches, ensures dependable operation even in the harsh environments typical of construction sites, ports, and steel mills – enduring vibration, dust, moisture, and temperature extremes where purely electronic sensors might falter.
- High Repeat Accuracy: Once correctly set, mechanical cam switches offer exceptional positional repeatability. The crane will consistently stop at precisely the same angles every time the limit is reached, crucial for repetitive operations.
- Simplicity & Ease of Understanding: The direct mechanical link and clear switching action make the principle easy for technicians and inspectors to comprehend, troubleshoot, and maintain without requiring highly specialized diagnostic tools.
- Clear Positive Action: The physical actuation of a heavy-duty switch provides a definitive, unambiguous signal to the crane’s control system. There’s no ambiguity or signal drift – the circuit opens or closes decisively.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to complex sensing systems offering similar positional limits (like absolute encoders with processing units), mechanical rotary limit switches provide critical safety functionality at a highly competitive cost.
Where Crane Rotary Limit Switches are Essential
You’ll find these indispensable devices deployed wherever precise rotational control and safety are paramount:
- Tower Cranes: Essential for slewing upper structure limits to prevent collisions with other structures or cranes, especially on congested sites. They are mandatory safety components defined by standards like ISO 12485.
- Mobile Cranes (Specific Models): Used to limit boom swing or superstructure rotation on models where unrestricted rotation poses a risk.
- Overhead Cranes (Rotating Types): Applied on ladle handling cranes, rotary gantries, or any overhead crane where the bridge or trolley incorporates rotation.
- Shipbuilding & Heavy Fabrication: Critical in goliath cranes and other specialized lifting equipment within massive fabrication halls. Ensuring boom swing stays within safe boundaries around delicate structures or other work areas is vital.
- Ports & Terminals: Used on ship-to-shore (STS) gantry cranes and other port equipment to manage rotational travel limits near vessels and infrastructure.
Ensuring Peak Performance: Installation and Maintenance
The reliability of a crane rotary limit switch hinges on correct installation and diligent upkeep:
- Precise Installation: The switch must be securely mounted to prevent movement or vibration loosening. The input shaft connection to the rotating crane structure must have zero backlash or slippage – any play here translates to inaccurate positioning and potential safety failures. Alignment is critical.
- Initial Calibration: After installation, the switch must be meticulously calibrated. This involves physically rotating the crane to its desired limits and adjusting the internal cams so they trigger the microswitches exactly at those positions.
- Regular Maintenance Schedule: Like all critical safety components, periodic inspection and testing are mandatory. This includes:
- Checking mounting bolts and shaft couplings for tightness.
- Inspecting switch contacts for signs of arcing, wear, or contamination.
- Testing the functionality by slowly slewing the crane towards its limits to ensure the switch activates correctly and promptly stops movement.
- Verifying any position feedback signals (if equipped).
- Lubricating shafts and moving parts as per manufacturer specifications. Never lubricate switch contacts.
- Environmental Protection: While inherently robust, ensure conduit entries are sealed and the unit is protected from severe impacts or excessive ingress of water/corrosive agents.
Selecting the right rotary limit switch involves careful consideration of the crane type, required torque capacity on the input shaft (based on crane size and inertia), the number