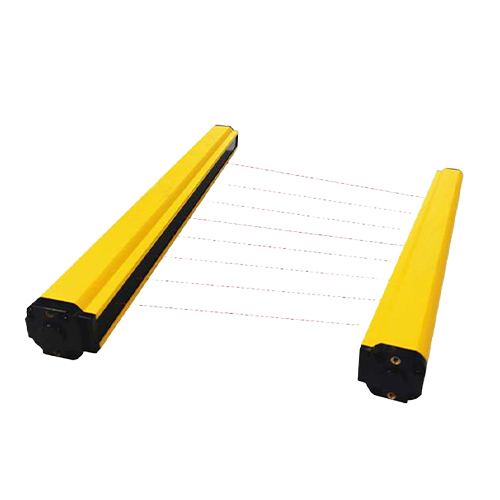
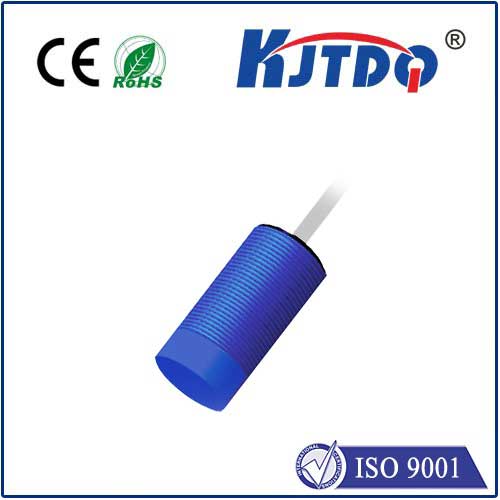
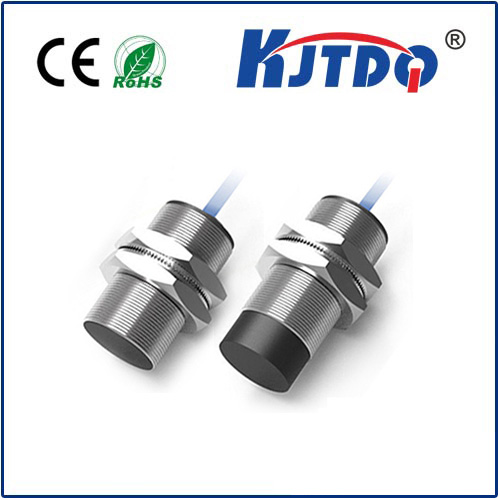
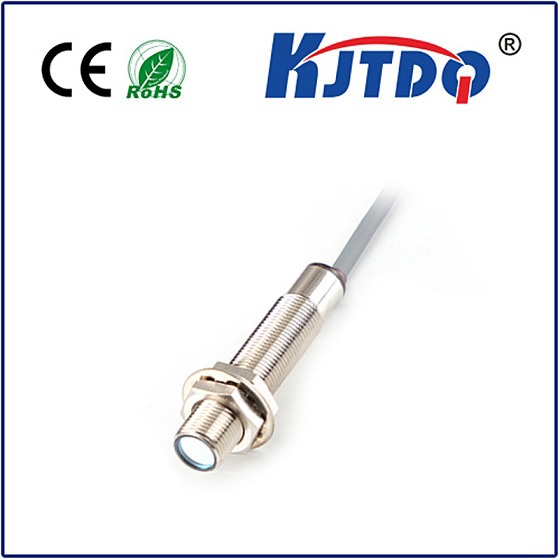
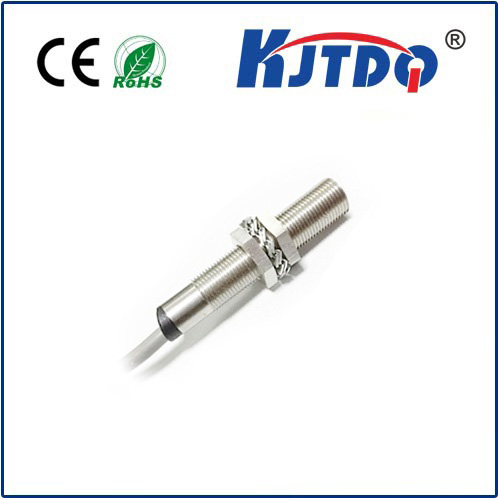
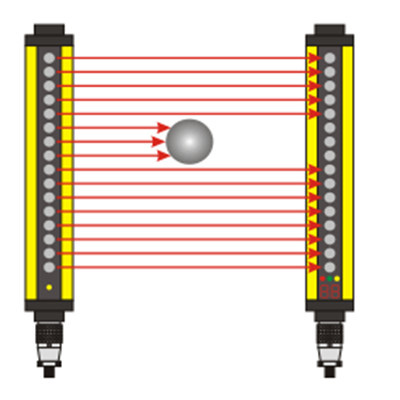
A belt slipper is a device used to monitor whether the belt is slipping in a belt drive system. Its working principle is usually mainly based on the following methods:
· Combined sensor detection: This method uses multiple sensors installed on the belt to determine whether slipping occurs by detecting the movement status of the belt. The sensor can be a pressure sensor, speed sensor or infrared sensor, etc. When the belt slips, the sensor will capture the abnormal movement state and trigger an alarm or alarm signal.
· Dynamic model monitoring: This method is based on the dynamic behavior of the belt drive system to detect slippage. By establishing a dynamic model, changes in parameters such as belt speed, tension, and torque are monitored. When the belt slips, these parameters will change abnormally. By comparing with the model under normal conditions, it can be determined whether slippage has occurred.
Sound or vibration detection: When the belt slips, a specific sound or vibration will be generated. Changes in these signals are detected by installing sound or vibration sensors. When the signal exceeds a preset threshold or is significantly different from the baseline under normal conditions, it can be determined that slippage has occurred.
It should be noted that the specific detection principles will vary depending on different equipment and applications. These methods are often combined to improve detection accuracy and reliability.